Plant Journal:中科院遗传所张劲松和陈受宜研究组发现转录调控在
2016年4月7日,国际植物学权威期刊《The plant Journal》在线发表中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所植物基因组学国家重点实验室张劲松研究组和陈受宜研究组发表的一篇研究文章,文章报道研究人员发现转录调控在大豆籽粒驯化过程中的重要作用。博士生陆翔是该论文的第一作者,张劲松研究员和陈受宜研究员为论文共同通讯作者。
大豆是我国重要的粮食作物和经济作物,高百粒重和高油含量是栽培大豆重要的农艺性状和驯化特征。因此研究大豆的驯化机制,对于改善大豆的品质和增加大豆产量具有非常重要的意义。
研究人员针对驯化过程中发育大豆种子的转录组特征展开了全面而深入的研究。通过测定和分析栽培大豆和野生大豆发育种子的40个转录组数据并通过基因共表达网络分析发现,在驯化过程中基因表达量及共表达网络发生了显著变化,且基因表达量与网络衔接显著相关。3个基因集群模块系统的基因表达量在栽培大豆中比野生大豆中显著增加。其中2个基因集群模块系统的基因表达量与网络衔接显著相关。从这2个基因集群中鉴定了栽培大豆特异的2个调控籽粒油分和粒重的共表达网络。通过分析基因共表达网络并结合已知的QTL位点信息,发现赤霉素合成基因GA20OX和转录因子基因NFYA的启动子变异导致了它们的基因表达量变化。基因功能分析和关联分析表明,这2个基因的表达变化与种子百粒重和油含量呈正相关(图1)。这项研究揭示了大豆中通过基因表达进行籽粒性状选择的驯化机制,对于大豆育种具有潜在实际意义。
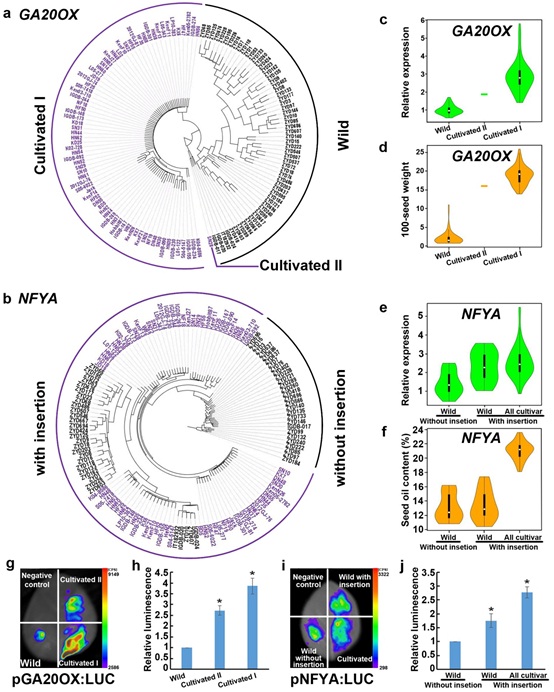
图1. 大豆GA20OX和NFYA基因启动子聚类分析及单倍型与基因表达和籽粒性状的关系。a, GA20OX基因启动子聚类分析。紫色名称表示栽培型大豆,黑色表示野生大豆。Cultivated I和Cultivated II及Wild表示不同的启动子单倍型。b, NFYA启动子聚类分析。紫色名称表示栽培型大豆,黑色表示野生大豆。With insertion: 启动子含有1500bp插入片段。Without insertion:启动子没有1500bp插入片段。c, GA20OX不同单倍型启动子与基因表达的关系。d, GA20OX不同单倍型启动子与百粒重的关系。e, NFYA不同单倍型启动子与基因表达的关系。f, NFYA不同单倍型启动子与油分含量的关系。g, GA20OX不同单倍型启动子活性分析。h, (g)中GA20OX不同单倍型启动子活性的定量分析。i, NFYA不同单倍型启动子活性分析。 j, (i)中NFYA不同单倍型启动子活性的定量分析。
原文链接:
The transcriptomic signature of developing soybean seeds reveals genetic basis of seed trait adaptation during domestication
原文摘要:
Cultivated soybeans have undergone many transformations during domestication. In this study, we report a comprehensive assessment of the evolution of gene co-expression networks based on the analysis of 40 transcriptomes from developing soybean seeds in cultivated and wild soybean accessions. We identified 2,680 differentially expressed genes during seed maturation and established two cultivar-specific gene co-expression networks. Through analysis of the two networks and integration with quantitative trait locus data, we identified two potential key driversGA20OX and NFYA for seed trait formation. GA20OX encodes an enzyme in a rate-limiting step of GA biosynthesis, and NFYA encodes a transcription factor. Overexpression of the GA20OX andNFYA enhanced seed size/weight and oil contents respectively in seeds of transgenic plants. The two genes showed significantly higher expressions in cultivated soybeans than those in wild soybeans, and the increases in expression were associated with the genetic variations in the promoter region of the two genes. Moreover, the expressions of the GA20OX and NFYA in seeds of soybean accessions correlated with seed weight and oil contents respectively. Our study reveals transcriptional adaptation during soybean domestication and may identify a mechanism of selection by expression for seed trait formation, providing strategies for future breeding practice.
作者:张劲松和陈受宜

