水稻:农科院钱前研究组与曾大力研究组发现影响水稻糙米率的重
近日,国际知名刊物《(RICE)》杂志上在线发表中国农业科学院水稻研究所种质创新团队钱前研究员、曾大力研究员的一篇研究论文,论文指出研究人员分离了影响水稻糙米率的重要QTL基因qBRR-10,该QTL对水稻糙米和颖壳的发育起到关键性调控作用,将有利于提高稻米在稻谷产量中的比重。任德勇博士和饶玉春博士为共同第一作者,钱前研究员、曾大力研究员为共同通讯作者。
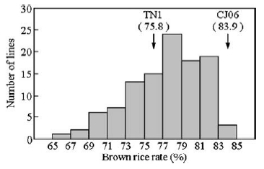
谷粒包含糙米(可食用)和颖壳(不可食用)两个部分。在超高产育种中,通过增加糙米率提高稻米实际产量和品质必将成为一种新型高效的育种手段。研究团队利用低糙米率品种TN1和高糙米率品种CJ06杂交的DH群体,通过QTL分析和高世代回交群体,在第10染色体上获得了一个主效糙米率QTL基因qBRR-10。进一步研究发现,来自CJ06的qBRR-10等位基因增加了谷粒的厚度和降低了颖壳的比重。通过深入挖掘qBRR-10的确切座位和分子标记辅助选择等手段,将为培育出糙率高和优质新品种提供新线索。
原文链接:
Fine Mapping Identifies a New QTL for Brown Rice Rate in Rice (Oryza Sativa .)
原文摘要:
Background
High yield and quality determine the commercial potential of rice variety. Brown rice rate (BRR) is a key factor ensuring grain yield and quality in rice. So far, there were few reports about the GENEs that directly controlled the BRR in rice.
Therefore, dissecting the genetic mechanism of the BRR genes can facilitate improving effective rice supply or edible grain yield.
Results
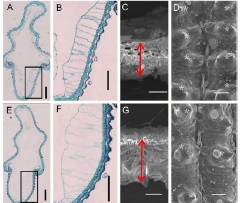
A double haploid population derived from the cross between Taichung Native 1 (TN1) (an indica variety) and Chunjiang 06 (CJ06) (a japonica variety) was used to investigate the genetic basis of grain milling and appearance traits affecting the BRR. By using a constructed molecular linkage map, four quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for the BRR were detected on chromosomes 1, 8, 9, and 10, respectively. In addition, three QTLs for appearance traits, including grain weight and grain length/width ratio, were detected on chromosomes 6, 9 and 10, respectively. Chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) were established at the qBRR-10 locus. Finally, the qBRR-10 was narrowed to a 39.5 kb region on chromosome 10. In this region, two candidate genes, LOC_Os10g32124 and LOC_Os10g32190, showed significantly differential expression in TN1 and CSSL1-2 compared with CJ06. Histocytological analysis suggested that cell size and hull thickness may be important factors for the BRR.
Conclusion
In the study, the qBRR-10 affected the BRR and was finally located to a region between two markers, P13 and P14. Two candidate genes were selected based on the expression difference between two parents, which facilitated the further cloning of the qBRR-10 gene and largely contributed to improve the grain yield and quality in rice.
doi: 10.1186/s12284-016-0076-7
作者:钱前、曾大力

