Plant Cell:沙特学者发表植物mRNA监控系统研究成果
2016年2月17日,国际植物学著名期刊《The Plant Cell》杂志上在线发表了沙特阿卜杜拉国王科技大学熊黎明研究组与中国农业科学院生物所植物分子生物学研究室陈涛博士合作的一篇研究论文,研究人员介绍了在植物mRNA监控系统研究中取得新研究进展。生物技术研究所陈涛博士为论文共同第一作者,沙特阿卜杜拉国王科技大学熊黎明研究员为论文通讯作者。
无义介导的mRNA降解(nonsense-mediated mRNA decay,NMD)是真核细胞中重要mRNA监控机制,识别并降解开放阅读框中含有提前终止密码子(premature termination codon,PTC)的mRNA,以避免因截短的蛋白产物积累对细胞造成毒害。
FIERY2是一个去磷酸化酶,它与能控制RNA Pol II的C末端磷酸化水平的磷酸化酶同源。以前的实验发现,FIERY2能控制HOS5的磷酸化水平进而影响了pre-mRNA剪切和micrornA产生(见前期研究PLoS Genetics,2013和Nucleic Acids Research,2015)。研究发现FIERY2能和NMD的核心组分eIF4AIII和UPF3相互作用并控制eIF4AIII的去磷酸化,并且通过加入STA(激酶抑制剂)可以在fry2-1突变体内恢复eIF4AIII的磷酸化平衡。而eIF4AIII的磷酸化水平决定了其在细胞内的定位,正确的核内定位是eIF4AIII行使功能所必须的。进一步通过位点突变找到了控制eIF4AIII定位的氨基酸位点。通过RNA-seq分析发现NMD识别对象在fry2-1突变体内显著积累,此积累可用蛋白激酶抑制剂在fry2-1突变体内恢复。上述研究工作系统地揭示FIERY2通过控制eIF4AIII磷酸化水平调控植物mRNA质量控制体系的作用机制。
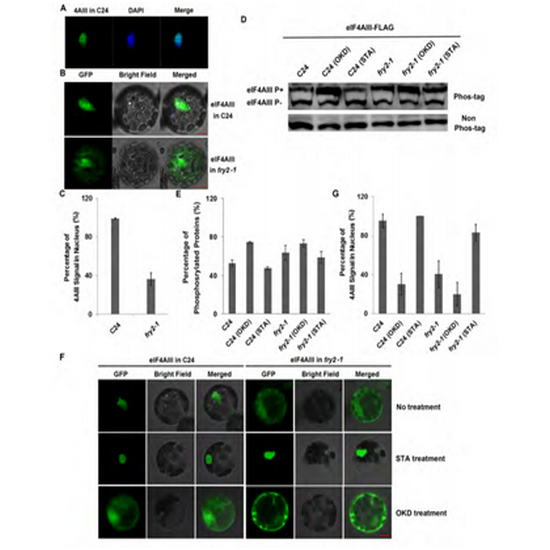
图:FIERY2通过控制eIF4AIII磷酸化水平调控植物mRNA质量控制体系的作用机制
原文链接:
The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase-like protein FIERY2/CPL1 interacts with eIF4AIII and is essential for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in ArABIdopsis
原文摘要:
Nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) is a posttranscriptional surveillance mechanism in eukaryotes that recognizes and degrades transcripts with premature translation-termination codons (PTCs). The RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase-like protein FIERY2 (FRY2, also known as CPL1) plays multiple roles in RNA processing in Arabidopsis. Here, we found that FRY2 interacts with two NMD factors, eIF4AIII and UPF3, and is required for the dephosphorylation of eIF4AIII, which retains eIF4AIII in the nucleus and limits its cytoplasmic accumulation. By analyzing newly generated rna-seq data combing with quantitative RT-PCR validation, we identified that a subset of alternatively spliced transcripts and 5'-extended mRNAs with NMD-eliciting features were commonly accumulated in the fry2-1 mutant, cycloheximide-treated wild type and upf3 mutant plants, indicating that FRY2 is essential for the degradation of these NMD transcripts.
作者:陈涛

