ACS Nano:北京大学孙育杰组利用超高分辨显微揭示活细胞转录工厂
2016年2月8日,国际著名期刊《ACS Nano》杂志在线发表北京大学生命科学学院生物动态光学成像中心孙育杰课题组题为“Study of RNA Polymerase II Clustering inside Live-Cell Nuclei Using Bayesian Nanoscopy”的文章,首次通过新型超分辨成像技术(贝叶斯超分辨显微术)实现了活细胞单个转录工厂(RNA Pol II cluster)的动态过程观测和定量分析。北京大学博士生陈轩泽,北京大学技术员魏冕,北京大学本科生郑鸣是这篇论文的并列第一作者,北京大学生物动态光学成像中心孙育杰研究员是该论文的通讯作者。
哺乳细胞的细胞核是一个高度复杂的自组装结构,染色质是其主要成分。已有大量证据表明基因表达调控过程经常伴随着染色质结构的动态变化,这可能是基因表达调控的一个更高级的层面。以转录工厂(transcription factory)模型为例,该模型最早在1993年提出,基于电镜和免疫荧光的数据发现大量RNA Pol-II集合的位点,多个基因被招募到这些转录工厂共转录。然而到目前为止这个模型还存在很大争议,最主要的原因是研究手段的限制。之前的数据主要依赖于电镜和荧光显微镜,电镜虽然分辨率高,但没有动态信息;荧光显微镜则没有足够的分辨率。实现对转录工厂RNA Pol II cluster的动态定量观测对其机理的研究有重要意义。通过发展和应用贝叶斯超分辨率显微技术,孙育杰课题组首次在活细胞的细胞核内原位观察到了单个转录工厂的组装和解聚的动态过程,并且测量了活细胞内转录工厂的数目和大小随时间以及细胞环境的影响。揭示了转录工厂产生和消失的异质性,支持了转录工厂产生的on-demand模型,证明了转录工厂在pre-elongation phase招募Pol II 分子。这一成像分析方法也可以应用到其他纳米尺度的活细胞核内动态观测研究中。

贝叶斯超分辨解析纳米尺度转录工厂空间分布
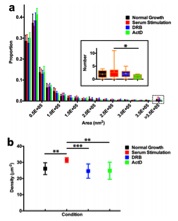
转录工厂在pre-elongation phase招募Pol II 分子
原文链接:
Study of RNA Polymerase II Clustering inside Live-Cell Nuclei Using Bayesian Nanoscopy
原文摘要:
Nanoscale spatiotemporal clustering of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) plays an important role in transcription regulation. However, dynamics of individual Pol II clusters in live-cell nuclei has not been measured directly, prohibiting in-depth understanding of their working mechanisms. In this work, we studied the dynamics of Pol II clustering using Bayesian nanoscopy in live mammalian cell nuclei. With 50 nm spatial resolution and 4 s temporal resolution, Bayesian nanoscopy allows direct observation of the assembly and disassembly dynamics of individual Pol II clusters. The results not only provide quantifications of Pol II clusters but also shed light on the understanding of cluster formation and regulation. Our study suggests that transcription factories form on-demand and recruit Pol II molecules in their pre-elongation phase. The assembly and disassembly of individual Pol II clusters take place asynchronously. Overall, the methods developed herein are also applicable to studying a wide realm of real-time nanometer-scale nuclear processes in live cells.
作者:孙育杰

