华南植物园提出未来对植物组蛋白去甲基化酶研究方向
华南植物园农业及资源植物研究中心罗鸣博士等对植物组蛋白去甲基化酶的分类及在植物生长发育过程中的功能进行综述,并提出未来对植物组蛋白去甲基化酶的研究方向。相关文章发表于2013年10月的《Plant molecular Biology Reporter》杂志上。
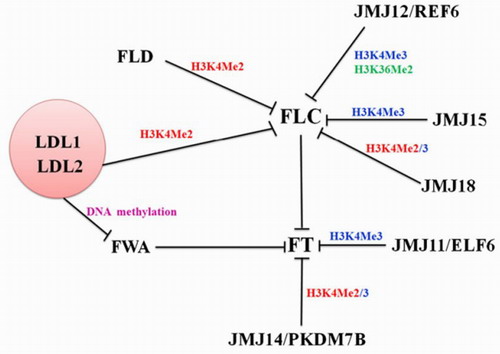
图示:拟南芥组蛋白去甲基化酶通过抑制重要开花基因FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC) 或 FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) 表达调控植物开花时间
近年来,随着大量表观遗传现象的发现与报道,植物表观遗传学已经成为植物分子生物学的研究热点。表观遗传修饰不改变生物体DNA的序列,通过DNA的甲基化,组蛋白修饰和染色质重塑等途径调节基因的表达。其中,组蛋白修饰方式包括组蛋白的乙酰化、甲基化、磷酸化和泛素化等。
组蛋白甲基化水平受组蛋白甲基转移酶和组蛋白去甲基化酶的调控,研究表明组蛋白去甲基化酶(histone lysine demethylases, KDMs)在植物生长发育过程发挥重要作用。
华南植物园农业及资源植物研究中心罗鸣博士等综述了植物组蛋白去甲基化酶的分类及在植物生长发育过程中的功能,以及组蛋白去甲基化酶通过调节植物基因表达参与植物开花时间调控、花和叶片的发育、油菜素内酯信号转导途径等方面的表观遗传机制,并提出了未来对植物组蛋白去甲基化酶的研究方向。
该研究得到国家重点基础研究发展计划“973计划”、国家自然科学基金、广东省自然科学基金及中科院植物资源保护与可持续利用重点实验室基金等的资助。
原文摘要:
Histone Lysine Demethylases and Their Functions in Plants
Ming Luo,Fu-Yu Hung, Songguang Yang, Xuncheng Liu, Keqiang Wu
Histone methylation—transfer of methyl groups to lysines or arginines residues of histone tails—plays an important role in the regulation of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Histone methylation levels are regulated by histone methyltransferases and histone demethylases. There are two types of histone lysine demethylases (KDMs) in eukaryotes: KDM1/LSD1-like and JmjC domain-containing demethylases. KDMs can regulate gene expression directly through histone modification or indirectly through DNA methylation and siRNA regeneration. Recent studies indicate that KDMs play important regulatory roles in plant growth and developmental processes such as flowering time control, hormone response and circadian regulation.

