BMC Plant Biol:农科院水稻所黄世文和张健研究组发表水稻表观遗传
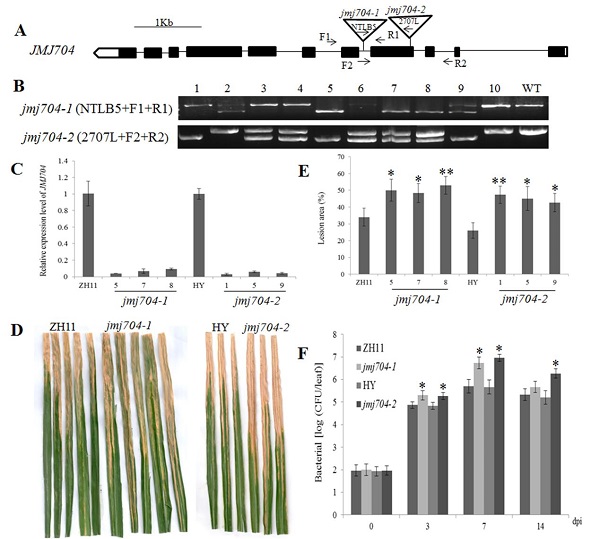
近日,《BMC plant biology》杂志在线发表中国农业科学院水稻研究所黄世文和张健研究员联合发表的研究文章,研究所团队合作研究发现了水稻jmjC组蛋白脱甲基化酶JMJ704能够正向调节水稻对白叶枯病原菌( Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Xoo)侵染的防御反应。侯雨萱博士为第一作者,黄世文和张健两位研究员为通讯作者。
表观遗传调控(Epigenetic regulation)是指在不改变基因DNA序列的前提下,通过共价修饰基因的DNA或附着的组蛋白来激活或抑制该基因的转录。作为植物的新卫士,表观遗传调控在植物抗病防御反应中的功能正日益被人们所熟知。水稻jmjC家族编码一系列的组蛋白脱甲基化酶。前人研究表明该家族成员JMJ705通过激活水稻Xoo抗性的正调节子的表达而调控水稻的抗性。该研究证实,JMJ704通过减少水稻Xoo抗性负调节子的H3K4me2/3水平来抑制负调节子的表达,进而正向调控水稻的抗性。这一结果揭示了一个与前人报道截然不同的新机制,表明jmjC介导的水稻抗性依赖于正调控子上调和负调控子下调的双向通路。
原文链接:
JMJ704 positively regulates rICE defense response againstXanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae infection via reducing H3K4me2/3 associated with negative disease resistance regulators
原文摘要:
Background
Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing proteins are a group of functionally conserved histone lysine demethylases in Eukaryotes. Growing evidences have shown that JmjCs epigenetically regulate various biological processes in plants. However, their roles in plant biotic stress, especially in rice bacterial blight resistance have been barely studied so far.
Results
In this study, we found that the global di- and tri-methylation levels on multiple lysine sites of histone three were dramatically altered after being infected by bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Xoo infection induced the transcription of 15 JmjCs, suggesting these JmjCs are involved in rice bacterial blight defense. Further functional characterization of JmjC mutants revealed that JMJ704 is a positive regulator of rice bacterial blight resistance as the jmj704 became more susceptible to Xoo than the wild-type. In jmj704, the H3K4me2/3 levels were significantly increased; suggesting JMJ704 may be involved in H3K4me2/3 demethylation. Moreover, JMJ704 suppressed the transcription of the rice defense negative regulator genes, such as NRR, OsWRKY62 andOs-11N3, by reducing the activation marks H3K4me2/3 on them.
Conclusions
JMJ704 may be a universal switch controlling multiple GENEs of the bacterial blight resistance pathway. JMJ704 positively regulates rice defense by epigenetically suppressing master negative defense regulators, presenting a novel mechanism distinct from its homolog JMJ705 which also positively regulates rice defense but via activating positive defense regulators.
作者:黄世文和张健

