PNAS:中科院动物所谭铮研究组发现具有环境响应能力的新型核酸
近日,PNAS杂志在线发表中国科学院动物研究所谭铮研究组发表的一篇研究文章,研究组发现了一种具有环境响应能力的新型核酸G-四链体结构。第一作者为博士生李新敏,通讯作者为郑克威和谭铮。
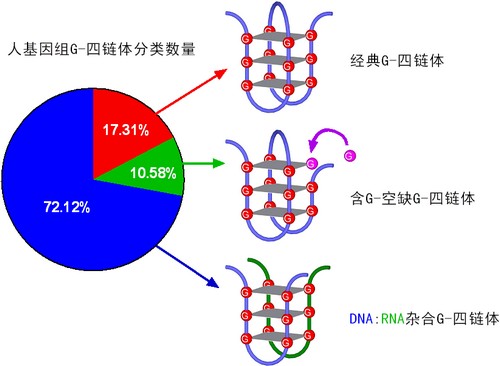
除了传统的DNA双螺旋,富含鸟嘌呤的核酸分子可以形成四股链的G-四链体结构。能够形成G-四链体的序列在基因组DNA中广泛存在并在恒温动物启动子附近聚集。这一现象提示G-四链体具有调控基因表达的生物学功能。在过去20余年中,人们所研究的核酸G-四链体(经典G-四链体)主要是由4段含有3个及以上连续G的分子内结构。
谭铮研究组于2013年发现了一种在转录中由DNA非模板链和所转录的RNA共同形成的新型G-四链体结构,即DNA:RNA杂合G-四链体。研究组最近又发现一种具有环境响应能力的新型核酸G-四链体结构。这种新G-四链体的结构特征是在G-quartet平面上含有G-空缺,它可以从环境中吸收一个含Guanine碱基的分子而形成一个更加稳定的结构。这种被命名为GVBQ(G-vacancy-bearing G-quadruplexes,含G-空缺G-四链体)的G-四链体可以在单链核酸和转录的双链DNA中形成。它具有响应原核和真核细胞的生理浓度的GMP和GTP的能力并可以借此影响DNA聚合酶的DNA复制活性。生物信息学分析发现这类结构在原核和真核基因中有特殊的分布规律,提示它们可以在细胞中形成并与基因表达调控有关。
与经典G-四链体相比,研究组所发现的DNA:RNA杂合G-四链体和含G-空缺G-四链体具有的独特性质是它们能够响应生理过程或生理状态,进而进行相关调控。例如DNA:RNA杂合G-四链体在转录中形成又反过来调节转录活性。含G-空缺G-四链体可能通过响应GMP和GTP的生理浓度而感知细胞的代谢状态,改变调节能力。根据目前的统计,研究组所发现的DNA:RNA杂合G-四链体和含G-空缺G-四链体数量在人基因组占到了三种G-四链体的80%以上。这两种新G-四链体的生理响应能力和数量表明它们是人基因组中具有更大生理调控潜能的主流G-四链体结构。
研究组相关的G-四链体其它方面研究组亦获得两项进展。
博士生吴壬乙在活细菌中检测到了DNA:RNA杂合G-四链体的形成和它对转录造成的中断,并发现杂合G-四链体相对于经典G-四链体是导致转录中断的主要因素。这一发现表明杂合G-四链体可以在活细胞中形成并具有干预细胞转录活性的能力。该工作以吴壬乙为第一作者于2015年发表于Angew Chem Int Ed。
另外博士生刘珈泉发现转录诱导产生的G-四链体具有DNA链的极性化,即它倾向在非模板链上形成而不在模板链上形成。这一结果表明RNA聚合酶具有决定G-四链体形成的能力,同时也说明不同链上的G-四链体可能有不同的生理活性。该工作以刘珈泉为第一作者于2015年发表于Angew Chem Int Ed,并被评为VIP(Very Important Paper)。
新型核酸G-四链体结构
原文链接:
Guanine-vacancy–bearing G-quadruplexes responsive to guanine derivatives
原文摘要:
G-quadruplex structures formed by guanine-rich nucleic acids are implicated in essential physiological and pathological processes and nanodevices. G-quadruplexes are normally composed of four Gn (n ≥ 3) tracts assembled into a core of multiple stacked G-quartet layers. By dimethyl sulfate footprinting, circular dichroism spectroscopy, thermal melting, and photo-cross-linking, here we describe a unique type of intramolecular G-quadruplex that forms with one G2 and three G3 tracts and bears a guanine vacancy (G-vacancy) in one of the G-quartet layers. The G-vacancy can be filled up by a guanine base from GTP or GMP to complete an intact G-quartet by Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding, resulting in significant G-quadruplex stabilization that can effectively alter DNA replication in vitro at physiological concentration of GTP and Mg2+. A bioinformatic survey shows motifs of such G-quadruplexes are evolutionally selected in genes with unique distribution pattern in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms, implying such G-vacancy–bearing G-quadruplexes are present and play a role in gene regulation. Because guanine derivatives are natural metabolites in cells, the formation of such G-quadruplexes and guanine fill-in (G-fill-in) may grant an environment-responsive regulation in cellular processes. Our findings thus not only expand the sequence definition of G-quadruplex formation, but more importantly, reveal a structural and functional property not seen in the standard canonical G-quadruplexes.
作者:谭铮

