Biogeosciences:中科院武汉植物园揭示流域土地利用对湖泊脱氮功能
欧洲地球科学联盟EGU主办的学术期刊Biogeosciences发表中国科学院武汉植物园揭示流域土地利用对湖泊脱氮功能的研究结果。
土地利用变化对区域水环境乃至全球气候变暖都存在着显著影响。反硝化过程能有效降低水体中的氮含量以及富营养化水平,是浅水湖泊最重要的脱氮途径。前人研究已经阐明水质、底泥性质以及水生植物的群落结构都可能在一定程度上影响湖泊的反硝化脱氮能力,但到目前为止,学术界对流域土地利用影响湖泊反硝化过程的机理还缺乏基本了解。
中国科学院武汉植物园的刘文治、姚璐和刘贵华等科研人员测定了长江中下游地区20个浅水湖泊67个底泥样品的潜在反硝化、背景反硝化、N2O产量以及相对N2O产量等参数。研究发现,流域土地利用对湖泊水质和底泥性质都存在显著性影响,但对水生植物的多样性及生物量没有影响。底泥的反硝化和N2O产量仅仅与水质参数显著相关。结构方程模型(SEM)分析表明流域内的人类活动(包括农业和城市土地利用)主要通过改变水质来影响湖泊底泥的反硝化能力和N2O产量。
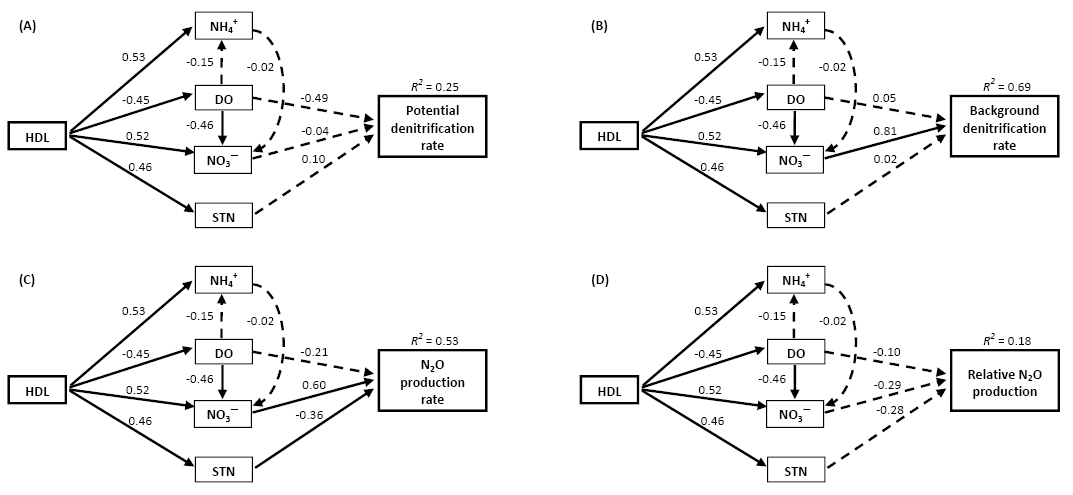
流域人类活动(HDL)影响湖泊底泥反硝化和N2O产量的路径分析
原文链接:
human land uses enhance sediment denitrification and N2O production in Yangtze lakes primarily by influencing lake water quality
原文摘要:
Sediment denitrification in lakes alleviates the effects of eutrophication through the removal of nitrogen to the atmosphere as N2O and N2. However, N2O contributes notably to the greenhouse effect and global warming. Human land uses (e.g. agricultural and urban areas) strongly affect lake water quality and sediment characteristics, which, in turn, may regulate lake sediment denitrification and N2O production. In this study, we investigated sediment denitrification and N2O production and their relationships to within-lake variables and watershed land uses in 20 lakes from the Yangtze River basin in China. The results indicated that both lake water quality and sediment characteristics were significantly influenced by watershed land uses. N2O production rates increased with increasing background denitrification rates. Background denitrification and N2O production rates were positively related to water nitrogen concentrations but were not significantly correlated with sediment characteristics and plant community structure. A significant positive relationship was observed between background denitrification rate and percentage of human-dominated land uses (HDL) in watersheds. Structural equation modelling revealed that the indirect effects of HDL on sediment denitrification and N2O production in Yangtze lakes were mediated primarily through lake water quality. Our findings also suggest that although sediments in Yangtze lakes can remove large quantities of nitrogen through denitrification, they may also be an important source of N2O, especially in lakes with high nitrogen content.
作者:刘贵华

