Plant Mol Biol:中科院东北地理所杨素欣研究组发表控制大豆种子大
10月19日plant molecular biology 杂志上在线发表中国科学院北地理所大豆分子设计育种重点实验室杨素欣研究员的关于大豆种子大小基因的研究成果,博士生赵宝添为论文第一作者,研究员冯献忠和杨素欣为论文责任作者。
种子的大小是决定大豆产量的重要因素之一,但在过去90年的世界大豆育种实践中,通过增加种子的大小提高大豆产量机理的研究进展比较缓慢。中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所大豆功能基因组学学科组的研究人员通过多年的努力,克隆了控制种子大小的GmCYP78A72基因,过量表达该基因可以使大豆的种子增加10%以上。该研究为进一步阐明大豆种子大小调控机制奠定了基础,该基因不仅可以被广泛地用于增加大豆不同品种的种子大小,而且可以采用类似的策略通过遗传改良其他作物的种子大小来提高其产量。
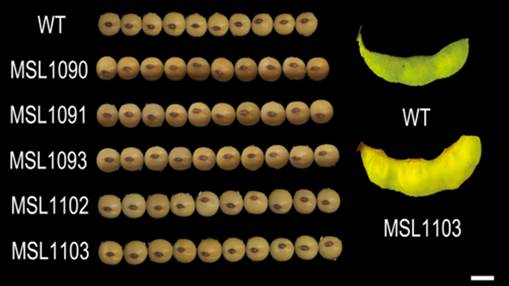
WT为野生型大豆,MSL1090、MSL1091、MSL1092、MSL1102和MSL1103为过量表达GmCYP78A72基因的不同株系。
原文链接:
ArABIdopsis KLU homologueGmCYP78A72 regulates seed size in soybean
原文摘要:
Soybean (Glycine max) is one of the most important crops in the world, and its yield is largely determined by grain weight and grain size. However, the genes that regulate soybean seed size have not been identified. CYP78A, which is highly conserved within terrestrial plants, regulates organ development. In Arabidopsis, AtCYP78A5/KLU has been shown to determine seed size. In the present study, soybean CYP78A72 (GmCYP78A72), one of the orthologs of KLU, was over-expressed in both Arabidopsis and soybean to examine its function in plant development.GmCYP78A72 heterologous expression in Arabidopsis resulted in enlarged sepals, petals, seeds and carpel. Over-expression of GmCYP78A72 in soybean resulted in increased pea size, which is an extremely desirable trait for enhancing productivity. Moreover, knock-down of GmCYP78A72does not reduce grain size. However, silencing of GmCYP78A57, GmCYP78A70 andGmCYP78A72 genes in triplet reduces the seed size significantly indicating functional redundancy of these three GmCYP78A genes. In conclusion, we investigated the role of CYP78A in soybean seed regulation, and our strategy can be effectively used to engineer large seed traits in soybean varieties as well as other crops.
作者:杨素欣

