Journal of Autoimmunity:中国科技大学廉哲雄课题组发表肝脏研究论文
近日,中国科技大学廉哲雄教授课题组在国际期刊《JouRNAl of Autoimmunity》上发表题为 “ Successful treatment of murine autoimmune cholangitis by parABIosis : Implications for hematopoietic therapy “ 的研究论文,揭示了在原发性胆汁性胆管炎中细胞治疗的新机制。
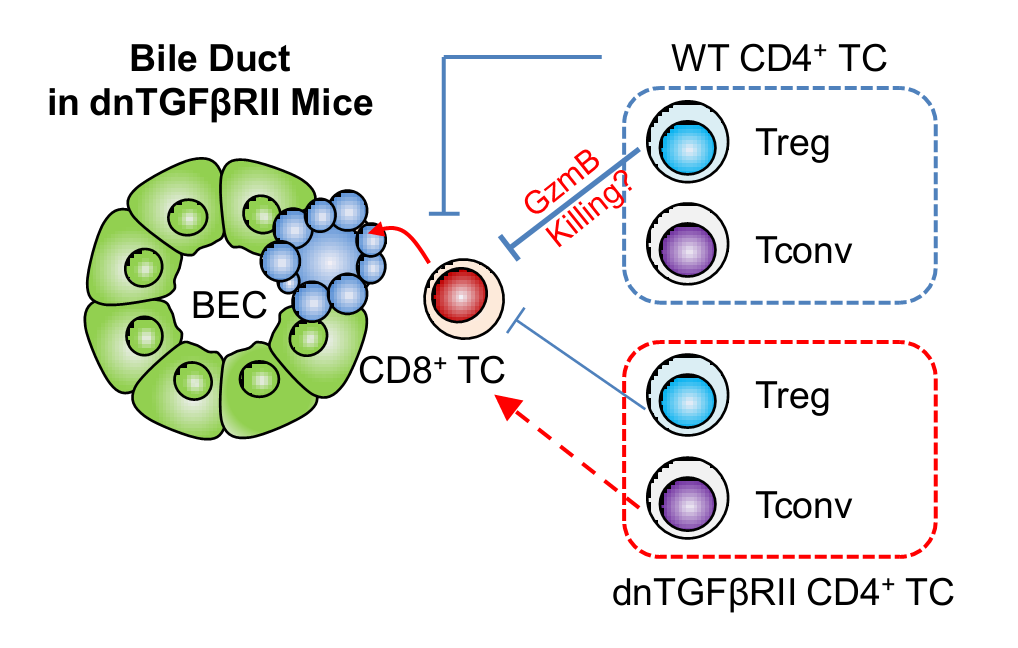
作为一种肝脏特异性的自身免疫性慢性疾病,原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)目前仍然缺乏有效的治疗手段。在该项研究中,课题组利用小鼠动物模型,模拟了人类PBC的发病情况,发现PBC的发病与CD4 t细胞的功能缺失有密切关系。进一步的研究工作中,通过骨髓嵌合以及连体共生的方法,尝试替换掉发病模型小鼠中的CD4 T细胞后,胆管浸润的致病性CD8 T细胞减少,PBC的疾病程度得以显著恢复,各项疾病指标都明显下降,表明CD4 T细胞的功能恢复有助于促进PBC疾病的治疗。
综上所述,该文介绍了CD4 T细胞在PBC疾病中的重要调节作用,为PBC疾病的治疗提供了可取的新思路和策略。
原文链接:
Successful treatment of murine autoimmune cholangitis by parabiosis: Implications for hematopoietic therapy
原文摘要:
There is a significant unmet need in the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) despite significant data on the effector pathways that lead to biliary duct damage. We focused attention on a murine model of PBC, the dominant negative transforming growth factor β receptor II (Tg) mice. To further define the pathways that lead to biliary pathology in these mice, we developed Tg mice deleted of CD4 cells (CD4−/−Tg).
Interestingly, these mice developed more severe cholangitis than control Tg mice. These mice, which lack CD4 cells, manifested increased levels of IFN-γ produced by effector CD8 cells. It appears that increased cholangitis is due to the absence of CD4 Treg cells. Based on these data, we parabiosed CD4−/−Tg mice with established disease at 8–9 weeks of age with C57BL/6 control mice. Such parabiotic “twins” had a significant reduction in autoimmune cholangitis, even though they had established pathology at the time of surgery. We prepared mixed bone marrow chimera mice constructed from CD4−/−Tg and CD8−/− mice and not only was cholangitis improved, but a decrease in terminally differentiated CD8+ T effector cells in the presence of wild type CD4 cells was noted. In conclusion, “correcting” the CD4 T cell subset, even in the presence of pathogenic CD8 T cells, is effective in treating autoimmune cholangitis.
doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2015.09.002
作者:廉哲雄

