华南植物园:荔枝果实衰老受miRNA调控
荔枝色泽鲜艳,营养丰富,具有较高的商业价值。然而,在采收后1-2天内荔枝就会变质,主要体现为果皮褐色。调控荔枝果实衰老的因素很复杂。micrornAs作为负调控因子参与了几乎所有的生理过程。在最新的一项研究中,中国科学院华南植物园植物资源保护与可持续利用重点实验室从miRNA水平探究了荔枝果实衰老和果皮褐变的机制。相关研究成果发表在7月刊的《BMC Plant Biology》上,朱虹副研究员是文章的共同第一作者,屈红霞研究员为文章通讯作者。
课题组选取常温贮藏和冷藏后货架期的荔枝果皮制备了5个小rna文库和1个降解组文库并进行测序分析(小RNA测序)和降解组测序分析( 由联川生物承担完成)。通过将小RNA测序读段与组装的荔枝unigene进行比对,首次在荔枝中鉴定到296个miRNAs,属于49个已知的miRNA家族。同时,鉴定到11个荔枝特异性miRNAs。通过降解组分析,鉴定到受167个已知miRNA剪切调控的197个靶基因,和3个荔枝特异性miRNAs调控的5个靶基因。综合茎环qRT-PCR和转录组表达谱分析,发现了14组miRNA-靶基因对参与了荔枝果实衰老相关的过程,包括能量调控,花青素代谢,激素信号通路以及抗病侵染等。
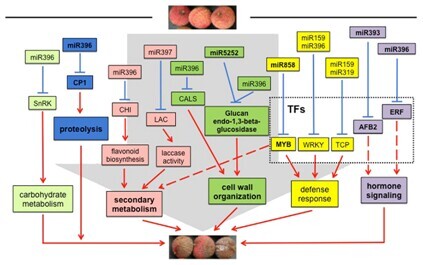
图1 荔枝果实衰老过程中的miRNA调控网络
本研究构建了一个调控荔枝果实衰老的miRNA-靶基因调控网络,揭示出在衰老荔枝果实中miRNA介导的调控机制。此项研究将有助于开发延缓荔枝果实和其他园艺产品衰老的新策略。
Abstract:BackgroundLitchi has a high commercial value due to its bright color and rich nutrients. However, it deteriorates with the pericarp turning brown within 1–2 days after harvest. The factors that mediate litchi fruit senescence are complicated. MicroRNAs act as negative regulators involved in almost every physiological process. To understand the mechanism of litchi fruit senescence and pericarp browning at the miRNA level, five small RNA libraries and a degradome library prepared from the pericarp of litchi fruit subjected to ambient storage and post-cold storage shelf life were sequenced.ResultsBy aligning the sRNA reads onto the litchi unigene assembly, 296 miRNAs belonging to 49 known miRNA families were first identified from litchi. In addition, 11 litchi-specific miRNAs were identified. Among these, 167 known miRNAs were identified to cleave 197 targets, and three litchi-specific miRNAs were found to have five targets. Through combined analysis of stem-loop quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and transcriptome profiling, 14 miRNA-target pairs were found to be actively involved in litchi fruit senescence-related processes, including energy regulation, anthocyanin metabolism, hormone signaling, and pathogen-infection defense.ConclusionsA network of miRNA-targets that regulate litchi fruit senescence has been proposed, revealing the miRNA-mediated regulation in senescent litchi fruit. This will aid in developing new strategies to postpone the senescence of litchi fruit and other horticultural products.
获取更多用户研究案例,请访问www.lc-bio.com或拨打免费咨询热线800-857-1452。
关于联川生物
联川生物成立于2006年,经过多年的快速发展,已成为业界领先的多组学技术服务商。公司拥有具有自主知识产权的µParaflo®微流体定制化芯片平台,可以为科研用户提供从基因组,转录组,到蛋白组的高通量定制化表达谱芯片解决方案。我们是全球首家提供microRNA表达谱芯片分析的服务商。作为国内最早提供高通量测序技术服务的公司之一,联川生物拥有经验丰富的技术团队和一流的生物信息学专家组,可以为研究人员提供多组学测序服务和深度个性化数据分析解决方案。为满足研究人员跨组学高通量研究需求,联川生物已将蛋白质组定量分析引入技术服务线,为用户提供贯穿中心法则的全程解决方案。多年来,联川生物一直与国内的科研团队保持着长期紧密的合作,助力科研人员在生物、医学、和农林领域的科学发现。全球科研用户使用联川生物的优质科研服务和高质量组学实验数据已发表了逾600篇高水平研究论文,其中已在Cell,Nature,Science系列顶级期刊上发表论文18篇。
作者:秩名

