PLOS ONE:华南农大张永亮教授揭示关联分析miRNA和mRNA表达谱揭示动
垂体前叶是调控动物产后生长最重要的内分泌器官,主要是通过控制生长激素(GH)基因转录,合成以及分泌。作为动物产后生长研究的理想模型,巴马小型猪相较于大型猪具有较低的生长性能和较少的个体差异。
在本项研究中,华南农业大学张永亮教授领衔的课题组采用miRNA芯片和mrna-seq对巴马小型猪和长白猪垂体前叶的miRNA和mRNA表达谱进行了关联分析。共检出222个miRNAs和12,909个转录本,这些miRNAs和mRNAs在两个品种中表现出较高的相关性(r>0.97)。实验鉴定到41个差异表达的miRNA和2,254个差异表达的转录本。通路分析表明,在两个品种中共有32个通路存在显著差异。值得注意的是,两个GH调节信号通路——cAMP和三磷酸肌醇(IP3),以及多个GH分泌相关的转录本在巴马小型猪中显著下调。进一步地,研究人员使用TargetScan和RNAhybrid预测了差异表达miRNAs(DE miRNAs)和差异表达基因(DE mRNAs)的相互作用。有趣的是,通过分析它们的变化倍数,发现大多数DE miRNA–DE mRNA靶基因对(63.68–71.33%)呈现负相关的表达模式。研究人员提出了一个可能的miRNAs,基因,和GH调控通路之间的网络。在这个网络中,研究人员采用双荧光素酶报告基因实验验证了两个miRNA-mRNA的相互作用(Y-47靶向FSHB;ssc-miR-133a-3p靶向GNAI3)。 此项研究将有助于更好地理解动物产后生长的潜在分子机制。
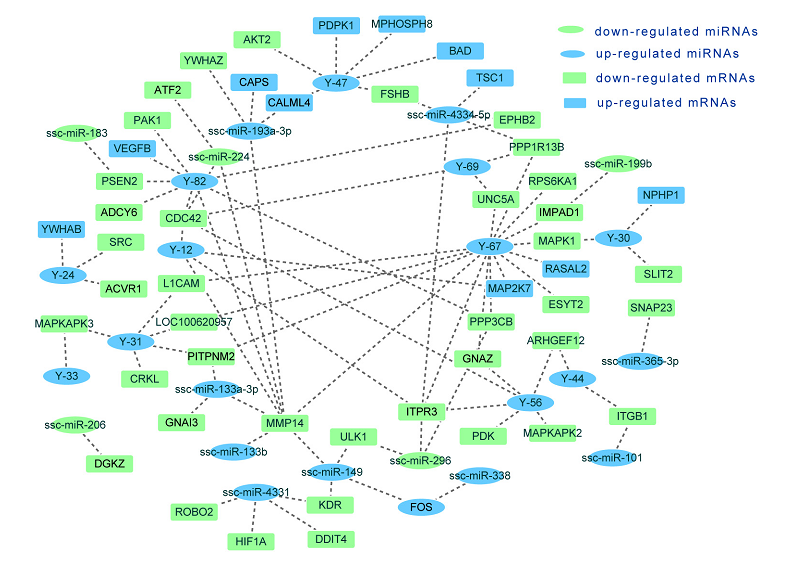
图1 潜在的动物生长调控网络
原文链接:
Comparative Anterior Pituitary miRNA and mRNA expression Profiles of Bama Minipigs and Landrace Pigs Reveal Potential Molecular Network Involved in Animal Postnatal Growth.
原文摘要:
The anterior pituitary is the most important endocrine organ modulating animal postnatal growth, mainly by controlling growth hormone (GH) gene transcription, synthesis, and secretion. As an ideal model for animal postnatal growth studies, the Bama minipig is characterized as having a lower growth performance and fewer individual differences compared with larger pig breeds. In this study, anterior pituitaries from Bama minipig and Landrace pig were used for miRNA and mRNA expression profile analysis using miRNA microarrays and mRNA-seq. Consequently, a total of 222 miRNAs and 12,909 transcripts were detected, and both miRNAs and mRNAs in the two breeds showed high correlation (r > 0.97). Additionally, 41 differentially expressed miRNAs and 2,254 transcripts were identified. Pathways analysis indicated that 32 pathways significantly differed in the two breeds. Importantly, two GH-regulation-signalling pathways, cAMP and inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate (IP3), and multiple GH-secretion-related transcripts were significantly down-regulated in Bama minipigs. Moreover, TargetScan and RNAHybrid algorithms were used for predicting differentially expressed miRNAs (DE miRNAs) and differentially expressed mRNAs (DE mRNAs) interaction. By examining their fold-changes, interestingly, most DE miRNA-DE mRNA target pairs (63.68-71.33%) presented negatively correlated expression pattern. A possible network among miRNAs, mRNAs, and GH-regulation pathways was also proposed. Among them, two miRNA-mRNA interactions (Y-47 targets FSHB; ssc-miR-133a-3p targets GNAI3) were validated by dual-luciferase assay. These data will be helpful in understanding the possible molecular mechanisms involved in animal postnatal growth.
doi: 10.1371/jouRNAl.pone.0131987.
作者:张永亮

