Journal of Immunology:上海巴斯德所发现调控I型干扰素表达和抗病毒
病毒是严重危害人类健康的杀手之一,I型干扰素是调节抗病毒免疫的关键因子。Toll样受体TLR3/4、RIG-I样受体和胞内DNA受体cGAS在感知病毒感染后,通过激活TBK1和IRF3,诱导I型干扰素的表达,但I型干扰素表达失调也会引起红斑狼疮等自身免疫性疾病。因此,深入了解机体对I型干扰素表达的分子调控机制,对于阐明传染病和自身免疫性疾病的致病机理,研发治疗这些疾病的新途径至关重要。
中国科学院上海巴斯德研究所免疫信号转导与调节研究组副研究员杜旻和硕士研究生刘晶华在研究员肖晖的指导下,通过筛选发现CK2在调控病毒诱导I型干扰素表达中起着关键性的作用。降低CK2的表达或抑制CK2的激酶活性,均导致细胞分泌大量的干扰素,增强抗病毒反应。在机理方面,CK2 广泛参与TLR3/4、RLR和cGAS诱导的信号通路,控制TBK1和IRF3的激活。此外,研究人员还发现使用CK2的小分子抑制剂TBB处理可以有效地激活TBK1,促进细胞分泌I型干扰素,阻止丙肝病毒、疱疹病毒等感染和复制,因此CK2有望作为治疗病毒感染的新靶点。
该项研究成果的研究论文Casein Kinase II Controls TBK1/IRF3 Activation in IFN Responses against Viral Infections(《蛋白激酶CK2调节病毒诱导的TBK1/IRF3活化和干扰素反应的作用与机制》)于5月1日发表在国际学术期刊《免疫学杂志》(The Journal of Immunology)上。
该研究获得国家重大科技专项“973”、国家自然科学基金、中科院“百人计划”、病毒学国家重点实验室等经费支持。
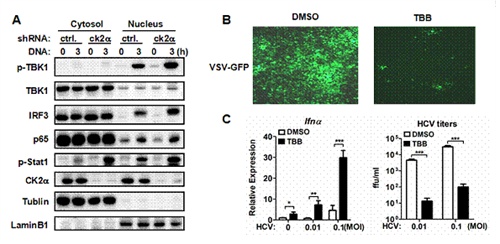
CK2负调控TBK1/IRF3磷酸化、IFN表达和抗病毒反应。(A) 基因敲降CK2后,DNA诱导的TBK1/IRF3磷酸化水平增高。 (B,C) 利用CK2抑制剂TBB能增强细胞的抗病毒能力。
原文链接:
Casein Kinase II Controls TBK1/IRF3 Activation in IFN Responses against Viral Infections
原文摘要:
By sensing viral nucleic acids, host innate receptors elicit signaling pathways converging on TBK1-IFN regulatory factor (IRF)3 axis in mediating IFN-αβ induction and defense mechanisms. In contrast, viruses have evolved with diverse immune evasion/interference mechanisms to undermine innate receptor signaling and IFN response. In this regard, approaches enabling host to overcome such immune evasion/interference mechanisms are urgently needed to combat infections by epidemic/pandemic viruses. In this study, we report that protein kinase CK2 serves as a key component controlling TBK1 and IRF3 activation in IFN-inducing TLR, RIG-I–like receptors, and cGAS/STING signaling pathways. Accordingly, knocking down of CK2 expression or genetic ablation of its kinase activity resulted in elevated IFN-αβ response in response to infection by DNA and RNA viruses. Moreover, PP2A was identified as one of the intermediate phosphatases responsible for CK2-regulated IFN response, suggesting that CK2 may regulate TBK1 and IRF3 activation indirectly. Importantly, blockade of CK2 activity by small molecule inhibitor was able to activate TBK1, whereby eliciting effective host defense mechanisms against hepatitis C virus infection. Taken together, our results identify CK2 as a novel regulator of TBK1 and IRF3 and suggest that targeting CK2 by small molecular inhibitor may be a viable approach to prevent and treat viral infections.
doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402777
作者:杜旻

