大鲵I型干扰素基因研究取得进展
近日,由中国水产科学研究院长江水产研究所陈倩、马杰博士为共同第一作者、曾令兵研究员为通讯作者,关于中国大鲵I型干扰素基因克隆测序、结构特性与表达特征分析以及抗病毒感染活性研究的论文在国际知名期刊《分子免疫学》上公开发表。
近年来,大鲵繁育与养殖业发展迅速,病害问题日渐突出,特别是大鲵虹彩病毒病对大鲵养殖业与物种保护带来了严重的危害,因此开展大鲵抗病毒干扰素基因研究具有潜在的应用价值。
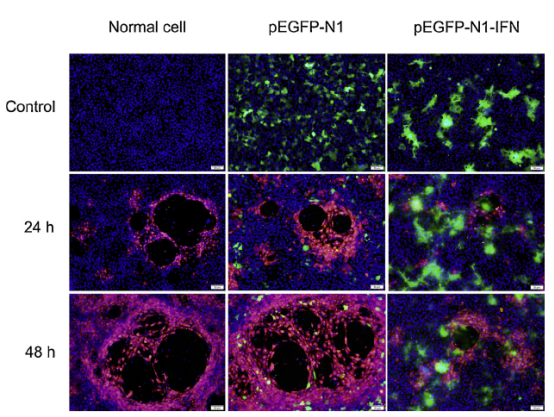
目前,除两栖类模式生物非洲爪蟾外,对其他两栖类动物的I型干扰素基因抗病毒功能鲜有研究。长江所鱼病研究团队在本项研究中成功克隆了中国大鲵I型干扰素全长基因。该研究首次在两栖类动物I型干扰素基因中发现了高等脊椎动物I型干扰素保守的CAWE 基序,为大鲵免疫系统分子进化研究提供了理论依据。在大鲵外周血白细胞中,发现Poly I:C诱导及大鲵虹彩病毒(GSIV)感染均能显著上调大鲵I型干扰素的表达,证实了该干扰素在抗病毒感染过程中发挥的重要作用。同时,体外细胞培养感染实验也证实,大鲵I型干扰素能显著抑制GSIV感染细胞的细胞病变效应形成,病毒的增殖过程在转录水平及翻译水平上均受到显著抑制。
长江所该项研究取得的重要进展,为进一步研究两栖类动物先天性免疫防御系统与抗病毒感染机制奠定了重要的基础。(来源:中国科学报 恩和)
Identification of Type I IFN in Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) and the response to an iridovirus infection
Abstract The type I IFNs play a major role in the first line of defense against virus infections. In this study, the type I IFN gene designated gsIFN was identified and characterized in the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). The genomic DNA of gsIFN contains 5 exons and 4 introns and has a total length of 5622bp. The full-length cDNA sequence of gsIFN is 1113bp and encodes a putative protein of 186 amino acids that has a 43% identity to type I IFN of Xenopus tropicalis. The deduced amino acid sequence has the C-terminal CAWE motif, that is mostly conserved in the higher vertebrate type I IFNs. Real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed broad expression of gsIFN in vivo and the highest level expression in blood, kidney and spleen. Additionally, the expression of gsIFN at the mRNA level was significantly induced in peripheral blood leucocytes after stimulation with poly I:C and after infection with the Chinese giant salamander iridovirus (GSIV). A plasmid expressing gsIFN was constructed and transfected into the Chinese giant salamander muscle cell line. Expression of the IFN-inducible gene Mx was up-regulated in the gsIFN-overexpressing cells after GSIV infection. The virus load and titer were significantly reduced compared with that in control cells. Additionally, a lower level of virus major capsid protein synthesis was confirmed by immunofluorescence assay compared to the control cells. These results suggest that the gsIFN gene plays an important role in the antiviral innate immune response.
原文链接:http://ac.els-cdn.com/S0161589015000553/1-s2.0-S0161589015000553-main.pdf?_tid=19f40458-d679-11e4-a09c-00000aab0f26&acdnat=1427677814_6e7c7a2979891852d36e6f5cee6670b8

