美科学家寄望玉米壳生产再生燃料

美国科学家今天说,已发现使用遭弃置玉米壳与叶柄制造廉价氢燃料的方法。这种燃料不会跟化石燃料一样污染环境。
(Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences)的研究报告指出,维吉尼亚理工暨州立大学(Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University)的研究团队取所得的进展,可以节省时间与金钱,并同时生产零排放燃料,未来可用于加速研发氢燃料汽车。
研究报告共同作者、维大生物系统工程部教授张以恒(Percival Zhang)说:“我们已经证明,往氢经济发展最重要的一步是,利用生物质资源,来制造可分散且负担得起的绿能氢气。”
报告说,研究进展是立基在之前使用木糖的研究,木糖“是最丰富的简单植物戊糖,可生产之前只在理论才能达到的氢气产能。”
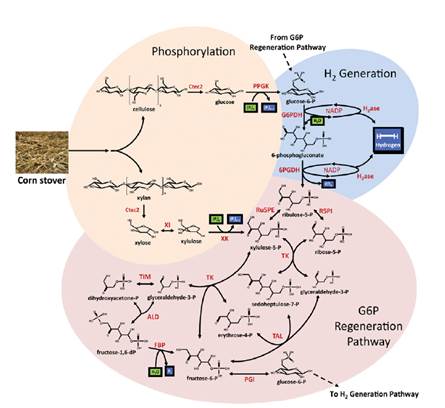
其他的氢燃料生产方法依赖高度加工的糖,但维大团队使用生物质玉米壳与叶柄,降低成本之外,生产燃料也变得更简单。 (来源:生物360)
High-yield hydrogen production from biomass by in vitro metabolic engineering: Mixed sugars coutilization and kinetic modeling
Abstract The use of hydrogen (H2) as a fuel offers enhanced energy conversion efficiency and tremendous potential to decrease greenhouse gas emissions, but producing it in a distributed, carbon-neutral, low-cost manner requires new technologies. Herein we demonstrate the complete conversion of glucose and xylose from plant biomass to H2 and CO2 based on an in vitro synthetic enzymatic pathway. Glucose and xylose were simultaneously converted to H2 with a yield of two H2 per carbon, the maximum possible yield. Parameters of a nonlinear kinetic model were fitted with experimental data using a genetic algorithm, and a global sensitivity analysis was used to identify the enzymes that have the greatest impact on reaction rate and yield. After optimizing enzyme loadings using this model, volumetric H2 productivity was increased 3-fold to 32 mmol H2•L−1•h−1. The productivity was further enhanced to 54 mmol H2•L−1•h−1 by increasing reaction temperature, substrate, and enzyme concentrations—an increase of 67-fold compared with the initial studies using this method. The production of hydrogen from locally produced biomass is a promising means to achieve global green energy production.
原文链接:http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2015/04/01/1417719112.full.pdf

