Plant Cell:中科院发现植物器官大小新机制
器官的发育需要经过细胞分裂、细胞分化和细胞生长等生物学过程,早期主要通过细胞分裂来增加细胞数目,后期主要通过细胞分化和细胞生长来增加细胞体积,从而形成了最终的器官大小。细胞分化过程常常伴随着细胞核内复制,然而细胞分裂、细胞分化和核内复制如何协同调控器官大小的分子机理并不清楚。
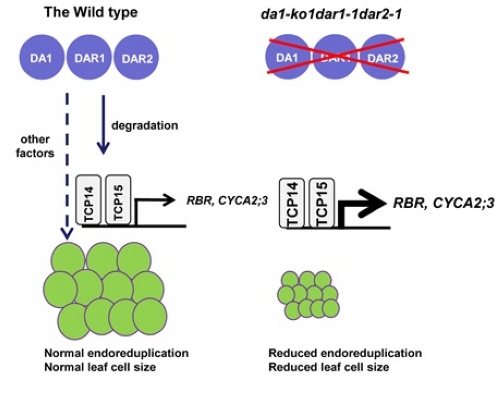
中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所李云海课题组主要从事植物器官大小调控的分子理论研究。该课题组前期研究表明,泛素受体DA1可以通过限制细胞分裂来调控器官的大小。为了进一步研究DA1及其同源基因的生物学功能,获得了DA1、DAR1 和DAR2 功能缺失突变体da1 dar1 dar2, 发现核内复制在da1 dar1 dar2 突变体中明显下调。
研究结果表明,DA1及家族成员DAR1和DAR2共同调控了植物细胞的核内复制,影响细胞分化和细胞大小。DA1、DAR1和DAR2与调控细胞周期基因的转录因子TCP14和TCP15在体内存在直接的相互作用,并调控TCP14和TCP15的蛋白稳定性。遗传学分析表明,DA1、DAR1和DAR2与TCP14、TCP15在调节核内复制、细胞和器官大小方面处于同一遗传途径。
这项研究成果揭示了DA1及其家族成员通过平衡细胞数目、细胞分化和细胞大小,从而决定器官大小的重要机制,对于深入理解植物器官大小调控的分子机理和提高植物产量等方面具有重要意义。该研究结果于3月10日在The Plant Cell上在线发表。李云海课题组的博士生彭元成和陈亮亮等为该论文的共同第一作者。该研究得到自然科学基金委和科技部的资助。
Although seed size is one of the most important agronomic traits in plants, the genetic and molecular mechanisms that set the final size of seeds are largely unknown. We previously identified the ubiquitin receptor DA1 as a negative regulator of seed size, and the Arabidopsis thaliana da1-1 mutant produces larger seeds than the wild type. Here, we describe a B3 domain transcriptional repressor NGATHA-like protein (NGAL2), encoded by the suppressor of da1-1(SOD7), which acts maternally to regulate seed size by restricting cell proliferation in the integuments of ovules and developing seeds. Overexpression of SOD7 significantly decreases seed size of wild-type plants, while the simultaneous disruption of SOD7 and its closest homologDEVELOPMENT-RELATED PcG TARGET IN THE APEX4 (DPA4/NGAL3) increasesseed size. Genetic analyses indicate that SOD7 and DPA4 act in a common pathway with the seed size regulator KLU to regulate seed growth, but do soindependently of DA1. Further results show that SOD7 directly binds to the promoter of KLUH (KLU) in vitro and in vivo and represses the expression ofKLU. Therefore, our findings reveal the genetic and molecular mechanisms ofSOD7, DPA4, and KLU in seed size regulation and suggest that they are promising targets for seed size improvement in crops.
作者:Yueying Zhang

