农科院植保所揭示蛋白泛素化调控水稻抗病新机制
泛素蛋白酶体系统(ubiquitin-proteasome system, UPS)是降解细胞内蛋白质的主要途径,与植物的生长发育及对生物和非生物胁迫反应密切相关。该系统主要由泛素活化酶(E1)、泛素交联酶(E2)、泛素连接酶(E3)和26S蛋白酶体组成,其中,E3连接酶决定底物的特异性,调控植物的生长发育及抗病过程。王国梁研究团队在前期研究中发现水稻基因SPL11是含有U-box和ARM repeat结构域的E3连接酶,负调控程序性细胞死亡和抗病防卫反应(Zeng et al., 2004, plant Cell),但SPL11的底物及其作用机制一直还不清楚。
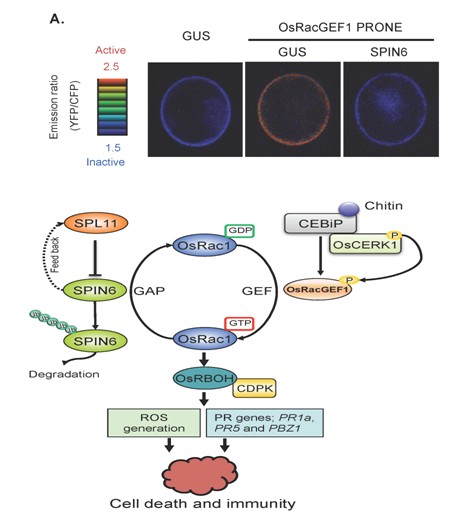
研究团队利用酵母双杂交技术,发现6个SPL11互作蛋白(SPIN1-6),其中SPIN6(Rho GTPase-activating protein, RhoGAP)是SPL11的底物,能够被SPL11通过UPS途径降解。更重要的是,该研究进一步揭示了SPIN6通过调节其底物小G蛋白OsRac1(水稻抗病系统的重要元件)的活性,负调控水稻免疫防卫反应。基于多年研究结果,研究团队提出了SPL11、SPIN6和OsRac1调控水稻防卫反应的工作模型。研究结果揭示了蛋白泛素化途径精确调控水稻抗病元件活性的分子机制,可为合理利用水稻抗性防治病害提供新思路和靶标。
相关研究结果于2015年2月6日以“The RhoGAP SPIN6 Associates with SPL11 and OsRac1 and Negatively Regulates Programmed Cell Death and Innate Immunity in Rice”为题在线发表在院选SCI顶尖核心期刊《PLoS Pathogens》(科学公共图书馆病原)上。论文第一作者刘金灵为湖南农业大学和中国农业科学院植物保护研究所联合培养博士生。该研究得到国家重点基础研究发展计划(973)项目、国家自然科学基金以及农科院创新工程的资助。
The ubiquitin proteasome system in plants plays important roles in plant-microbe interactions and in immune responses to pathogens. We previously demonstrated that the rice U-box E3 ligase SPL11 and its Arabidopsis ortholog PUB13 negatively regulate programmed cell death (PCD) and defense response. However, the components involved in the SPL11/PUB13-mediated PCD and immune signaling pathway remain unknown. In this study, we report that SPL11-interacting Protein 6 (SPIN6) is a Rho GTPase-activating protein (RhoGAP) that interacts with SPL11 in vitro and in vivo. SPL11 ubiquitinates SPIN6 in vitro and degrades SPIN6 in vivo via the 26S proteasome-dependent pathway. Both RNAi silencing in transgenic rice and knockout of Spin6 in a T-DNA insertion mutant lead to PCD and increased resistance to the rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae and the bacterial blight pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The levels of reactive oxygen species and defense-related gene expression are significantly elevated in both the Spin6 RNAi and mutant plants. Strikingly, SPIN6 interacts with the small GTPase OsRac1, catalyze the GTP-bound OsRac1 into the GDP-bound state in vitro and has GAP activity towards OsRac1 in rice cells. Together, our results demonstrate that the RhoGAP SPIN6 acts as a linkage between a U-box E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination pathway and a small GTPase-associated defensome system for plant immunity.
作者:Jinling Liu

