昆明植物所发现植物印迹基因新功能以及DNA甲基化相关性
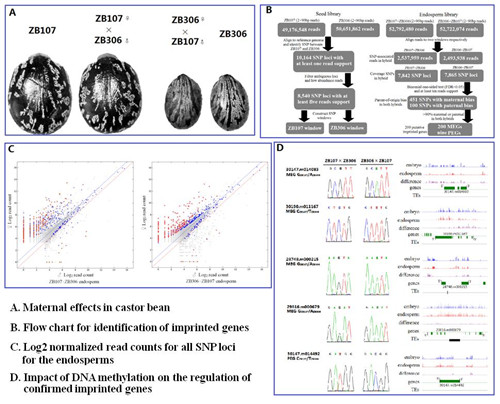
蓖麻基因组印迹以及其甲基化分析
基因组印记 (genetic imprinting)是一种非常重要的表观遗传学现象之一。在配子或合子发育过程中,来自亲本的等位基因或染色体发生了差异的表观修饰,导致了亲本等位基因的差异表达(即印迹基因)。在植物中基因组印迹主要发生在被子植物的三倍体胚乳组织中,且在胚乳以及种子的发育过程中扮演者重要的作用,但由于拟南芥胚乳随着种子发育很快消失,所以长期以来一直很难解析双子叶植物基因印迹对胚乳表型影响的生物学意义。
最近,中国科学院昆明植物研究所刘爱忠研究组的博士生徐伟利用典型双子叶胚乳型种子蓖麻,发展了崭新的研究体系,鉴别了大量新颖的印迹基因,通过系统分析植物印迹基因在进化过程的保守性发现了植物印迹基因具有很强的物种特异性。特别是通过基因组的甲基化分析,发现了基因印迹的发生和DNA甲基化密切相关,强烈暗示着DNA甲基化很可能是印迹基因发生的主要驱动力之一。
该研究不但极大地丰富了植物印迹基因及其功能的知识,而且为研究植物基因组印迹发生的生物学意义及其在单双子叶植物中的演化规律提供了重要的研究体系。
该研究的部分结果在线发表在Nucleic Acids Research上。研究得到中国科学院“百人计划”择优支持基金的资助。
原文摘要:
Wei Xu, Mengyuan Dai, Fei Li and Aizhong Liu
Genomic imprinting often results in parent-of-origin specific differential expression of maternally and paternally inherited alleles. In plants, the triploid endosperm is where gene imprinting occurs most often, but aside from studies on Arabidopsis, little is known about gene imprinting in dicotyledons. In this study, we inspected genomic imprinting in castor bean (Ricinus communis) endosperm, which persists throughout seed development. After mapping out the polymorphic SNP loci between accessions ZB306 and ZB107, we generated deep sequencing RNA profiles of F1 hybrid seeds derived from reciprocal crosses. Using polymorphic SNP sites to quantify allele-specific expression levels, we identified 209 genes in reciprocal endosperms with potential parent-of-origin specific expression, including 200 maternally expressed genes and 9 paternally expressed genes. In total, 57 of the imprinted genes were validated via reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction sequencing, and analysis of the genomic DNA methylation distribution between embryo and endosperm tissues showed significant hypomethylation in the endosperm and an enrichment of differentially methylated regions around the identified genes. Curiously, the expression of the imprinted genes was not tightly linked to DNA methylation. These results largely extended gene imprinting information existing in plants, providing potential directions for further research in gene imprinting.
作者:中科院

