南京古生物所等准噶尔盆地古植物及古地理学研究获进展
西准噶尔盆地泥盆纪古地理图
新疆北部准噶尔盆地西缘泥盆纪地层出露广泛,尤其是非常具有代表性的呼吉尔斯特组地层。呼吉尔斯特组地层因产有丰富的中泥盆世植物化石,而且保存良好,备受国内外学者关注。近年来,从该组地层中陆续发表和报道了数十种可代表中国北方区中泥盆世植物群的植物大化石。然而,由于新疆北部古生代构造运动频繁,地层往往不连续,对呼吉尔斯特组的时代,尤其是产有植物化石的一些产地与层位仍有一定的争议。
中国科学院南京地质古生物研究所研究员王怿、朱怀诚和徐洪河等长期以来与英国学者J. Marshall、C.Berry以及C. Wellman等进行志留纪—泥盆纪植物化石以及生物地层学等方面的合作研究,近年来也在新疆、云南等地开展了一系列的地层古生物学野外考察工作,采集并分析了大量岩石与化石样品。近日,该国际团队的研究成果之一发表在国际古植物学期刊Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology上。
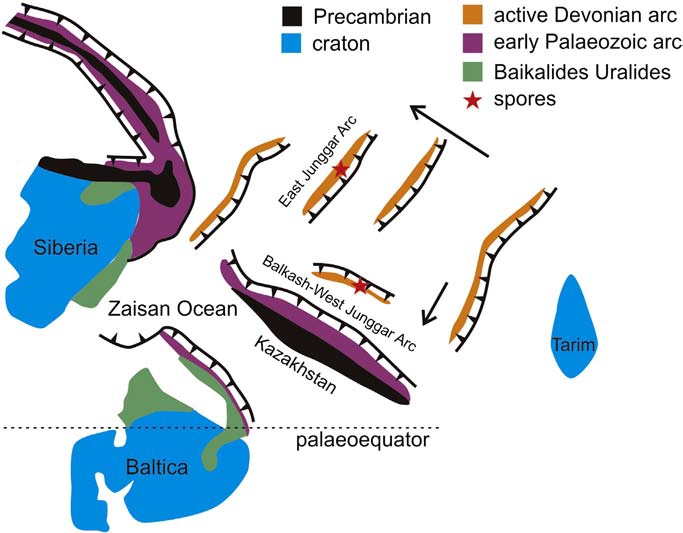
该研究通过对微体化石的分析与研究,论证了新疆北部准噶尔盆地西缘产有植物大化石的层位的地质时代,发现呼吉尔斯特组若干植物大化石层的时代涵盖了中泥盆世早期到晚泥盆世早期。文章也探讨了西准噶尔在泥盆纪,尤其是中泥盆世的构造演化历史。西准噶尔在泥盆纪时期属于哈萨克斯坦块体的若干火山岛弧之一,并不断向哈萨克斯坦块体俯冲,这与东准噶尔显著不同。泥盆纪西准噶尔独特的火山岛弧古地理格局对于物种的演化与传播具有重要意义。
原文摘要:
Xu, H.-H., Marshall, J.E.A., Wang, Y., Zhu, H.-C., Berry, C.M., Wellman, C.H
Devonian spores were systematically studied from four sections (251 Hill, G217 Highway, Hujiersite and Gannaren) in West Junggar, North Xinjiang, China. All four sections belong to, or are equivalent to, the Upper Member of the Hujiersite Formation, from which abundant plant macrofossils have also been reported. These spores enable us, for the first time, to date these fossil plant beds as from late Emsian to Frasnian in age. The plant localities are all from a Devonian volcanic terrain and have a lycopsid-dominant flora. These lycopsid plants have near global Devonian distributions and are hence the most mobile elements among the contemporary floras. In the upper part of the sequence (Givetian/Frasnian) very rare progymnosperms (both spores and some megafossils) were found. The West Junggar shows a different palynological asseMBLage from that of the East Junggar and is palaeogeographically significant.
标签: 准噶尔盆地古植物
作者:中科院

