中国学者在Cell Research发文揭示diRNA参与调控DNA损伤修复的新机制
中国学者在Cell Research发文揭示diRNA参与调控DNA损伤修复的新机制
DSB是真核生物基因组后果最严重的损伤,可以导致基因突变、基因组不稳定和细胞死亡,因此与包括癌症在内的多种疾病的发生密切相关。真核细胞已演化出了复杂的DSB修复机制,其涉及到一系列感应蛋白、传导蛋白和效应蛋白的协调作用。戚益军研究组首次报道了真核细胞中存在一类特异性受DSB诱导并在DSB修复中起到重要作用的小RNA,diRNA (DSB-induced small RNA) (Cell 149:101-112,2012;Cell 2012年度最佳论文)。 diRNA如何介导DSB修复尚不清楚。
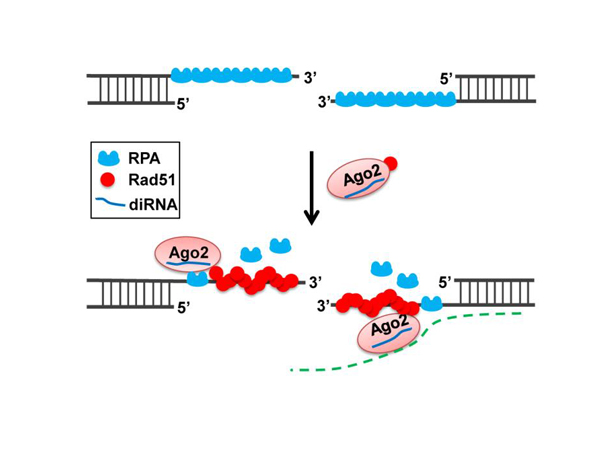
戚益军研究组与杨运桂研究组紧密合作,利用生化和细胞生物学等手段,研究发现diRNA只调控DSB的同源重组修复途径,而不影响非同源末端连接修复途径。这种特异性修复活性依赖于diRNA的效应蛋白Ago2。
他们进一步研究发现,Ago2可与同源重组修复重要因子Rad51形成复合物,并且Rad51在DSB位点的招募和同源重组修复活性取决于Ago2的催化活性及其结合小rna的能力。研究还发现,DSB末端的加工,RPA和Mre11在单链DNA末端的装载不受diRNA和Ago2调控,表明Ago2很可能通过直接调节Rad51的招募发挥作用。
这些研究结果表明,Ago2可能在diRNA的指导下,促进Rad51在DNA双链断裂位点的招募或滞留,从而调控同源重组活性,高效修复DNA损伤。
该研究进一步揭示了小RNA在DNA双链断裂修复过程中的保守性和重要功能,为后续从小RNA和DNA修复角度开展对人类疾病如恶性肿瘤发生发展研究提供了新思路。
该研究得到了清华-北大生命科学联合中心、中国科学院、科技部和国家自然科学基金委的资助。
原文摘要:
Ago2 facilitates Rad51 recruitment and DNA double-strand break repair by homologous recombination
Min Gao, Wei Wei, Ming-Ming Li, Yong-Sheng Wu, Zhaoqing Ba, Kang-Xuan Jin, Miao-Miao Li, You-Qi Liao, Samir Adhikari, Zechen Chong, Ting Zhang, Cai-Xia Guo, Tie-shan Tang, Bing-Tao Zhu, Xing-Zhi Xu, Niels Mailand, Yun-Gui Yang, Yijun Qi and Jannie M Rendtlew Danielsen
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are highly cytotoxic lesions and pose a major threat to genome stability if not properly repaired. We and others have previously shown that a class of DSB-induced small RNAs (diRNAs) is produced from sequences around DSB sites. DiRNAs are associated with Argonaute (Ago) proteins and play an important role in DSB repair, though the mechanism through which they act remains unclear. Here, we report that the role of diRNAs in DSB repair is restricted to repair by homologous recombination (HR) and that it specifically relies on the effector protein Ago2 in mammalian cells. Interestingly, we show that Ago2 forms a complex with Rad51 and that the interaction is enhanced in cells treated with ionizing radiation. We demonstrate that Rad51 accumulation at DSB sites and HR repair depend on catalytic activity and small RNA-binding capability of Ago2. In contrast, DSB resection as well as RPA and Mre11 loading is unaffected by Ago2 or Dicer depletion, suggesting that Ago2 very likely functions directly in mediating Rad51 accumulation at DSBs. Taken together, our findings suggest that guided by diRNAs, Ago2 can promote Rad51 recruitment and/or retention at DSBs to facilitate repair by HR.
标签: DNA损伤修复 diRNA 效应蛋白Ago2 Rad51
作者:生命中心

