中科院成都生物所中药提取物体外代谢研究获进展
中国科学院成都生物研究所的研究人员从整体的角度研究中药的代谢产物、代谢途径以及和酶诱导与抑制的关系,在中药混合物代谢、中药配伍相互作用以及活性物质基础等方面的研究显示出广泛的应用前景。 相关文章发表于《Anal Bioanal Chem》杂志上。
中科院成都生物所中药提取物体外代谢研究获进展
由于中药代谢的复杂性和分析检测手段的局限,其体外代谢研究大多针对某个或某些活性成分的代谢。但是,中药是多组分的复杂混合物,某一成分的代谢或各成分代谢的简单叠加都难以体现中药代谢的真实情况。
因此,对中药提取物的整体代谢研究可能为这一命题提供新思路。体外中药整体代谢研究,需要解决体外代谢效率以及复杂化学成分的分离和分析的难题。
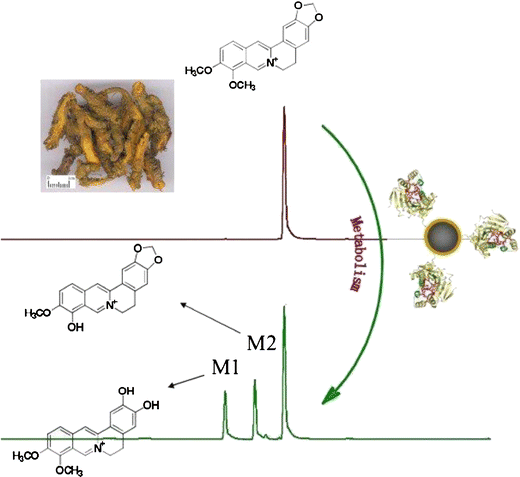
中国科学院成都生物研究所的研究人员以磁性纳米粒子为固定相,将肝微粒体固定在其表面制备的一种生物反应器,具有代谢效率高、方便样品分析的前处理、能够反复使用等优点。该生物反应器配合HPLC-MS等结构分析手段,在对中药提取物进行整体代谢的研究中表现出很大的优势。
以黄连提取物为研究对象,将其与该生物反应器共孵化以后,利用磁分离即实现生物反应器与反应溶液的分离;反应液直接经UPLC-MS/MS检测,鉴定了一系列反应物(黄连中的固有成分)与代谢产物,发现两个主要代谢产物峰—去亚甲基小檗碱和芬氏唐松草定碱,其中去亚甲基小檗碱是黄连主要成分小檗碱、巴马汀、药根碱、非洲防己碱的共同代谢产物。最后提出了黄连提取物整体代谢时各主成分的代谢途径。
该项研究从整体的角度研究中药的代谢产物、代谢途径以及和酶诱导与抑制的关系,在中药混合物代谢、中药配伍相互作用以及活性物质基础等方面的研究显示出广泛的应用前景。
原文摘要:
In vitro metabolic study of Rhizoma coptidis extract using liver microsomes immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles
Ying Xue, Jing Xiong, Hai-Li Shi, Yi-Ming Liu, Lin-Sen Qing, Xun Liao
Although metabolic study of individual active compounds isolated from herbal plants has been intensive, it cannot truly reflect the fate of herbs because the herbal extracts in use have many constituents. To address this problem, whole extracts of herbs should be investigated. Microsomes have been heavily used in the in vitro metabolic study of drugs, and various materials have been used to immobilize microsomes to develop highly effective and reusable bioreactors in this field. In this work, rat liver microsomes were immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles (LMMNPs) to develop a highly active and recoverable nanoparticle bioreactor. Using this bioreactor, we investigated the in vitro metabolism of Rhizoma coptidis extract. Incubation of berberine, a major active ingredient of R. coptidis, with LMMNPs for 20 min produced two metabolites, i.e., demethyleneberberine and thalifendine, at high levels. From a comparison of the time courses of thalifendine formation obtained by ultraperformance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis, it was found that LMMNPs had a higher BioLogical activity than free liver microsomes in metabolizing berberine. Further, the activity of LMMNPs remained almost unchanged after six consecutive uses in the incubation tests. Metabolism of R. coptidis extracts by LMMNPs was studied. The same two metabolites of berberine, i.e., demethyleneberberine and thalifendine, were detected. After a thorough study seeking support for this observation, it was found that demethyleneberberine was the common metabolite of five protoberberine-type alkaloids present in R. coptidis extract, including palmatine, jatrorrhizine, columbanine, epiberberine, and berberine.
标签: 中药提取物 代谢产物 代谢途径 酶诱导
作者:中科院 点击:次

