植物所水稻株型建成研究获进展
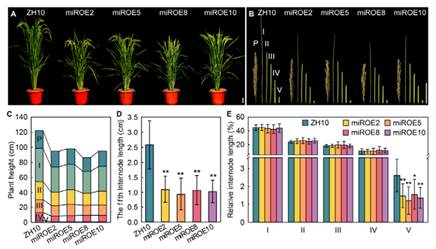
水稻株高和叶片夹角是构成理想株型的重要方面。在灌浆时期,直立的叶片可以使水稻植株接收更多光能、提高产量,因此对株型的分子设计是水稻育种的重要策略。国内外学者在水稻株型调控领域已取得一些进展,但仍有很多科学问题需要回答。
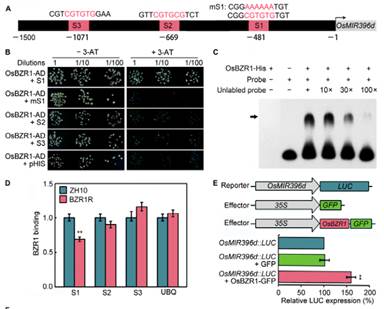
中国科学院植物研究所种康研究组发现水稻中,当 OsmiR396d 过量表达时,水稻呈现出叶夹角增大和部分矮化的表型。研究人员进一步通过生理学检测、生化手段验证和遗传学观察,证实油菜素内酯信号途径中的核心组分 OsBZR1 直接激活 OsMIR396d 基因的表达,OsmiR396d 分别控制靶基因 OsGRF4 与 OsGRF6 的转录;在对水稻的株高调控中,OsmiR396d 通过抑制 OsGRF6 的表达,导致赤霉素的合成与信号均减弱,引起水稻部分矮化表型;在调节水稻苗期叶夹角过程中,OsmiR396d 通过抑制 OsGRF4 而释放对油菜素内酯信号的抑制,正调控叶夹角。该研究进一步阐明,水稻中 miR396d 通过赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号途径调控水稻株高与叶夹角的分子机制,为理解植物激素精细调节水稻株型提供了新资料。
相关研究成果在线发表在 Plant Physiology上。研究工作得到了国家自然科学基金委和中科院战略性先导科技专项的资助。(来源:中国科学院植物研究所)
OsmiR396d miRNA affects gibberellin and brassinosteroid signaling to regulate plant architecture
Abstract Genetic improvement of plant architecture is one of the strategies for increasing the yield potential of rice (Oryza sativa). Although great progress has been made in the understanding of plant architecture regulation, the precise mechanism is still an urgent need to be revealed. Here, we report that over-expression of OsMIR396d in rice results in semi-dwarf and increased leaf angle, a typical phenotype of BR enhanced mutant. OsmiR396d is involved in the interaction network of BR and GA signal. In OsMIR396d over-expression plants, BR signaling was enhanced. In contrast, both the signaling and biosynthesis of GA were impaired. BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT1 (OsBZR1), a core transcription activator of BR signaling, directly promoted the accumulation of OsmiR396d which controlled BR response and GA biosynthesis by regulating the expression of different target genes respectively. GROWTH REGULATING FACTOR 6 (OsGRF6), one of OsmiR396d targets, participated in GA biosynthesis and signal transduction, but was not directly involved in BR signaling. This study provides a new insight into the understanding of interaction between BR and GA from multiple levels on controlling plant architecture.
原文链接:http://www.plantphysiol.org/content/plantphysiol/early/2017/11/27/pp.17.00964.full.pdf

