Mol Breeding:农科院作物所邹枨课题组等研发新型玉米分子育种芯片
2017年2月16日,中国农业科学院作物科学研究所“玉米分子育种技术和应用”创新团队邹枨副研究员在《molecular breeding》杂志上发表了题为“Development of a maize 55 K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding”的研究论文。论文报告了一款新型玉米55K分子育种芯片。该芯片由邹枨团队博奥晶典生物技术有限公司和南通新禾生物技术有限公司合作开发,芯片在提高基因组覆盖率的同时,加入了多种类型的功能性标记,将有助于提高基因挖掘和分子育种的效率。作物科学研究所博士生许诚和博奥晶典生物技术有限公司任永红为本文共同第一作者,邹枨副研究员和南通新禾生物技术有限公司的李平为本文共同通讯作者。
近十年来,随着测序技术的发展和成本的降低,DNA芯片在植物遗传育种中得到了广泛应用。作为重要的粮食和饲料作物,玉米具有丰富的遗传多样性,其多样性的检测不仅依赖于DNA芯片所含标记的数量,还取决于标记在基因组上的分布及其所含信息。当前,虽然已经有多款玉米芯片问世,但是这些芯片都存在以下不足,从而限制其分子育种应用:(1)玉米基因组覆盖率低,芯片位点分布不均衡;(2)芯片设计偏向于检测温带玉米的多样性,不适合热带玉米群体;(3)优良的稀有等位基因被淘汰;(4)以玉米单个自交系B73为参考基因组,造成玉米基因组多样性覆盖的不完整。
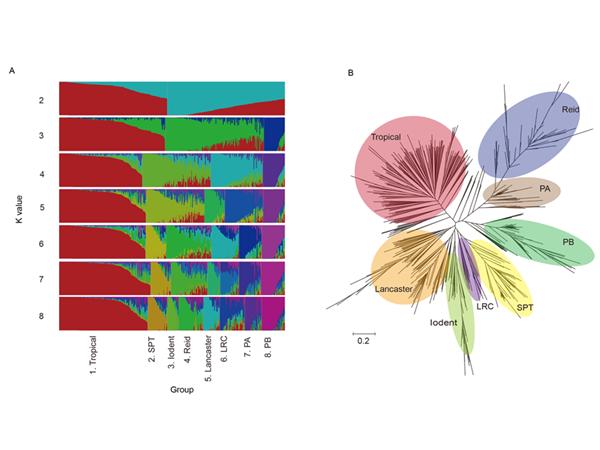
针对上述问题,该项研究对玉米55K分子育种芯片进行了一系列改进:一是从现有的两款芯片(Illumina MaizeSNP50 BeadChip, 600 K Affymetrix Axiom Maize Genotyping Array)和368份玉米的转录组测序数据中均匀挑选在温、热带玉米群体中均具有较高多态性的SNP位点。二是结合尚未公开发表的重测序数据,筛选来自于非B73参考基因组的4067个SNP位点。三是挑选了734个用于划分玉米杂种优势群和451个与玉米重要农艺性状相关的SNP位点。四是根据玉米中已公开的转基因事件开发的132个SNP位点。“玉米分子育种技术和应用”创新团队利用该芯片对593份具有丰富遗传多样性的玉米自交系进行了基因型分析,结果显示,与其他玉米SNP芯片相比,该芯片具有(1)更低的位点缺失率和杂合率;(2)能够清晰地划分中国的玉米杂种优势群;(3)在热带和温带玉米群体间不具有明显的偏向性。该芯片自问世以来已被多家科研单位和种业公司应用于数千份玉米品种(材料)的指纹鉴定、杂种优势群划分、基因定位和分子标记辅助选择,其中包括中国玉米核心自交系、CIMMYT重要热带种质、美国重要自交系的指纹分析。日前,该团队将本款芯片应用于玉米多杂种群体的全基因组关联分析并取得了重要进展。相关结果为玉米商业化分子育种奠定了基础,有关育种企业只需要对自身的育种材料进行分析,即可获得与全球温、热带玉米核心材料相比较的重要育种信息,同时附带提供所测试材料的转基因检测结果。
原文链接:
Development of a maize 55 K snp array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding
原文摘要:
With the decrease of cost in genotyping, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have gained wide acceptance because of their abundance, even distribution throughout the maize (Zea mays L.) genome, and suitability for high-throughput analysis. In this study, a maize 55 K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding was developed on an Affymetrix® Axiom® platform with 55,229 SNPs evenly distributed across the genome, including 22,278 exonic and 19,425 intronic SNPs. This array contains 451 markers that are associated with 368 known genes and two traits of agronomic importance (drought tolerance and kernel oil biosynthesis), 4067 markers that are not covered by the current reference genome, 734 markers that are differentiated significantly between heterotic groups, and 132 markers that are tags for important transgenic events. To evaluate the performance of 55 K array, we genotyped 593 inbred lines with diverse genetic backgrounds. Compared with the widely-used Illumina® MaizeSNP50 BeadChip, our 55 K array has lower missing and heterozygous rates and more SNPs with lower minor allele frequency (MAF) in tropical maize, facilitating in-depth dissection of rare but possibly valuable variation in tropical germplasm resources. Population structure and genetic diversity analysis revealed that this 55 K array is also quite efficient in resolving heterotic groups and performing fine fingerprinting of germplasm. Therefore, this maize 55 K SNP array is a potentially powerful tool for germplasm evaluation (including germplasm fingerprinting, genetic diversity analysis, and heterotic grouping), marker-assisted breeding, and primary quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and genome-wide association study (GWAS) for both tropical and temperate maize.
作者:邹枨

