Nature子刊:瑞典首次成功解析DNA聚合酶ɛ在合成新基因组时详细
瑞典于默奥大学的医学生物化学和生物物理学系研究人员采用X射线晶体衍射技术,首次成功解析DNA聚合酶ɛ合成新基因组时的详细结构。这一发现有助于揭示大肠癌和宫颈癌的致癌突变对DNA聚合酶ɛ的影响。相关文章发表于2013年12月02日的《Nature Structural and molecular Biology》杂志上。
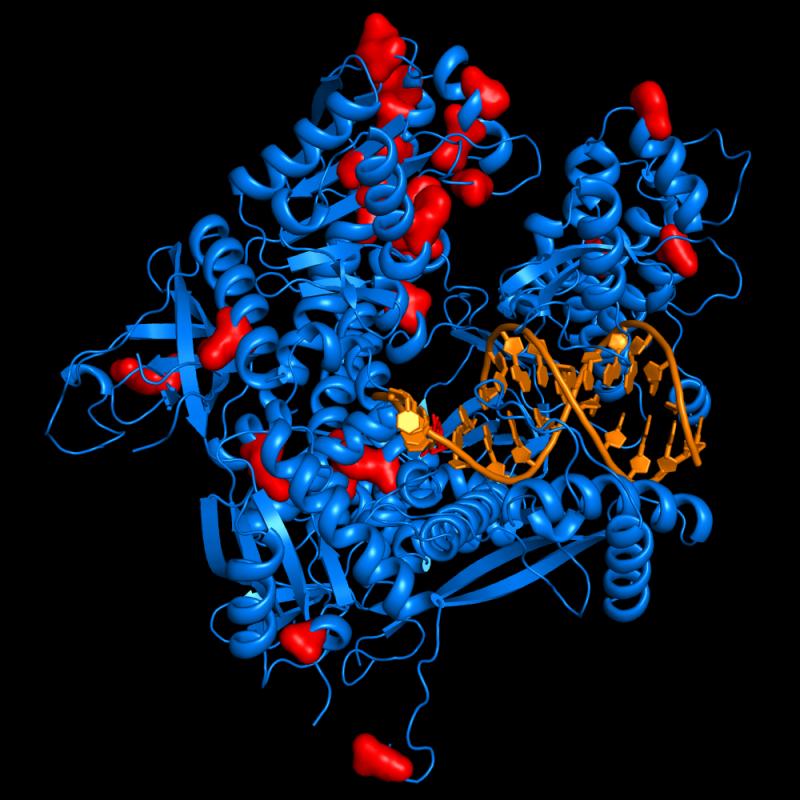
Nature子刊:瑞典首次成功解析DNA聚合酶ɛ在合成新基因组时详细结构
基因组由双链DNA组成,于默奥大学的科学家们在前期研究中发现,DNA聚合酶ɛ是真核生物中负责合成DNA新链的三个聚合酶之一。在基因组DNA的复制过程中,DNA聚合酶ɛ承担了约半数DNA的合成。这一过程既快又高度精确,以避免在合成时产生对细胞有害的突变。
研究人员采用X射线晶体衍射技术,对酿酒酵母的dna聚合酶ɛ进行高分辨成像。当DNA聚合酶ɛ合成DNA时,其催化中心会同时结合模板DNA和核苷酸原料,研究人员重点剖析了这一复合体的结构。
聚合酶B家族的高保真复制能力需要长β发夹结构,DNA聚合酶ɛ不具有这样的结构,但它却是家族中保真度最高的聚合酶。DNA聚合酶一旦脱落就需要重新开始,这会影响持续合成能力和复制的保真度。研究人员发现,DNA聚合酶ɛ的催化中心具有一个独特的结构域,可以使这种酶环绕新生的双链DNA,以避免脱落。
随后,研究人员进一步验证了这一模型,指出新结构域(称为P-domain)的确可以帮助聚合酶合成长链DNA而不脱落。DNA聚合酶ɛ的这一重要特性,使其能够在细胞分裂时高效完成复制基因组的任务。
许多科学家们都在对肿瘤细胞或遗传病家族的DNA进行测序,希望找到导致肿瘤或遗传病的突变。近年来这些项目显示,DNA聚合酶ɛ中的一系列突变,与大肠癌和宫颈癌的发展有直接关联。
“我们解析了DNA聚合酶ɛ的关键结构,在此基础上,人们可以分析上述突变对酶结构的改变,”文章的资深作者Erik Johansson教授说。“我们的研究可以帮助人们理解,特定突变对癌症发展的贡献。”
原文摘要:
Structural basis for processive DNA synthesis by yeast DNA polymerase ɛ
Matthew Hogg, Pia Osterman, Göran O Bylund, Rais A Ganai, Else-Britt Lundström, A Elisabeth Sauer-Eriksson & Erik Johansson
DNA polymerase ɛ (Pol ɛ) is a high-fidelity polymerase that has been shown to participate in leading-strand synthesis during DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. We present here a ternary structure of the catalytic core of Pol ɛ (142 kDa) from Saccharomyces cerevisiae in complex with DNA and an incoming nucleotide. This structure provides information about the selection of the correct nucleotide and the positions of amino acids that might be critical for proofreading activity. Pol ɛ has the highest fidelity among B-family polymerases despite the absence of an extended β-hairpin loop that is required for high-fidelity replication by other B-family polymerases. Moreover, the catalytic core has a new domain that allows Pol ɛ to encircle the nascent double-stranded DNA. Altogether, the structure provides an explanation for the high processivity and high fidelity of leading-strand DNA synthesis in eukaryotes.

