Nucleic Acids Res:北京生科院赵方庆研究组提出基因组重复区域组装
2016年12月6日,国际核酸类重要学术期刊《Nucleic Acids Research》杂志在线发表了中国科学院北京生命科学研究院计算基因组学实验室赵方庆团队题为The combination of direct and paired link graphs can boost repetitive genome assembly 的最新研究成果。该研究基于序列重叠部分构建了contig的直接连接信息图,并在其配对连接信息的帮助下,解决了由短片段重复序列造成的基因组拼接碎片化问题,在保证准确性的前提下延伸了序列的长度,获得了更完整、间隙更少的基因组序列。赵方庆课题组的史文聿和冀培丰为论文共同第一作者,赵方庆研究员为论文通讯作者。
一直以来,重复序列都是基因组拼接的主要限制因素,而富含短片段重复序列区域的组装更是难以跨越的障碍。这部分序列的缺失会导致基因断裂,使某些关键遗传信息在后续的研究分析中被遗漏。此前的序列组装算法仅仅使用配对连接信息,忽视了contig本身的连接关系,不仅使算法难度增加,而且拼接结果也存在间隙序列多、错误连接多等问题。特别是对于短片段重复序列,历来的组装算法都选择直接丢弃,使得短片段重复序列富集区域无法有效拼接。
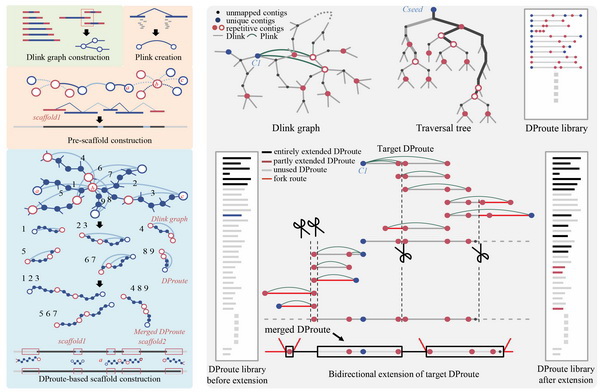
针对这种情况,赵方庆团队开发了基于直接连接信息的基因组组装算法inGAP-sf。该方法根据德布鲁因图的特征,基于contig的重叠部分构建了直接连接信息图,在配对连接信息的监督下拓扑路径,并对这些路径进行整合,同时引入了贝叶斯模型用于去除错误路径,从而得到高质量的拼接结果。通过在多个模拟数据和真实测序数据上的测试,inGAP-sf的结果与其他方法得到的拼接序列相比,连续性、准确性、完整性都有明显的提高。该研究使用的拼接策略极大程度地完善了已有序列组装算法的不足,为序列拼接提供了新的思路。inGAP-sf已发布在https://sourceforge.net/projects/ingap-sf,供相关研究人员使用。
inGAP-sf算法流程
原文链接:
The combination of direct and paired link graphs can boost repetitive genome asseMBLy
原文摘要:
Currently, most paired link based scaffolding algorithms intrinsically mask the sequences between two linked contigs and bypass their direct link information embedded in the original de Bruijn assembly graph. Such disadvantage substantially complicates the scaffolding process and leads to the inability of resolving repetitive contig assembly. Here we present a novel algorithm, inGAP-sf, for effectively GENErating high-quality and continuous scaffolds. inGAP-sf achieves this by using a new strategy based on the combination of direct link and paired link graphs, in which direct link is used to increase graph connectivity and to decrease graph complexity and paired link is employed to supervise the traversing process on the direct link graph. Such advantage greatly facilitates the assembly of short-repeat enriched regions. Moreover, a new comprehensive decision model is developed to eliminate the noise routes accompanying with the introduced direct link. Through extensive evaluations on both simulated and real datasets, we demonstrated that inGAP-sf outperforms most of the genome scaffolding algorithms by generating more accurate and continuous assembly, especially for short repetitive regions.
作者:赵方庆

