The Plant Cell:中科院微生物所邱金龙课题组发表植物MAPK信号转导机
2016年11月3日,国际植物科学顶级期刊《The Plant Cell》杂志在线发表了中国科学院微生物研究所邱金龙课题组在植物MAPK信号转导机制研究新进展文章,文章题为“MYB75 Phosphorylation by MPK4 Is Required for Light-Induced Anthocyanin Accumulation in Arabidopsis”。邱金龙课题组李盛楠博士及博士生王文义为文章的共同第一作者,邱金龙研究员为通讯作者。
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK)是真核生物整合胞外信号与细胞反应的重要信号枢纽。MAPK在跨膜受体的下游,通过磷酸化不同底物蛋白来激发特异的基因表达和细胞反应。因此,MAPK底物蛋白的研究将加深我们对植物感受外界信号后启动特异细胞反应机制的认识。然而,蛋白磷酸化的瞬时性给MAPK底物的鉴定造成了一定的困难。
邱金龙课题组创新性地利用组成型激活形式的MPK4为诱饵,筛选拟南芥酵母双杂交文库获得了其互作蛋白MYB75。MYB75是一种R2R3类转录因子,调控花青素的积累。研究发现,MPK4与MYB75在体内相互作用,且这种互作依赖于MPK4的激酶活性。MPK4参与了光诱导的花青素积累,与MPK4互作是MYB75调控花青素合成的功能所必需的。进一步研究发现,MPK4可被光信号激活。激活的MPK4磷酸化MYB75,且磷酸化主要发生在Thr126 和Thr131位点。磷酸化使MYB75蛋白的稳定性增加,从而显著促进花青素的合成。有趣的是,这种MYB75蛋白稳定性的增加并不依赖于E3泛素连接酶COP1。研究结果揭示了MPK4介导的MYB75磷酸化是光诱导的花青素积累所必需的。
作为最主要的环境信号之一,光影响植物的多个生理和代谢过程。目前,对植物光受体的研究相对清楚,但是光调节下游反应的信号转导机理仍然所知甚少。该项研究工作揭示了MAPK在光信号转导中发挥着重要作用。此外,该工作也为蛋白激酶底物的筛选和鉴定提供了新思路。
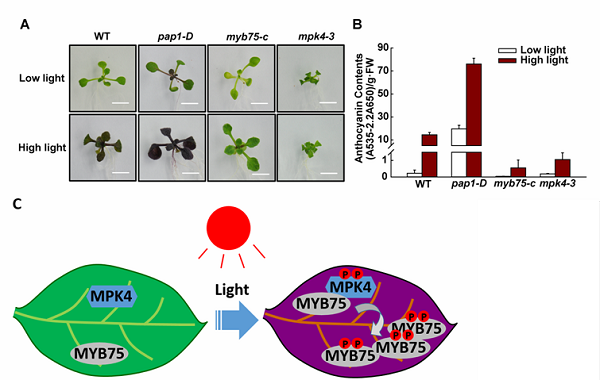
图例: MPK4调控光诱导的花青素积累
A.低光和高光下,拟南芥野生型及pap1-D,myb75-c及mpk4-3突变体花青素积累的表型;
B. 低光和高光下,拟南芥野生型及pap1-D,myb75-c及mpk4-3突变体花青素的含量;
C. MPK4调控光诱导的花青素积累机理的模式图。
原文链接:
MYB75 Phosphorylation by MPK4 Is Required for Light-Induced Anthocyanin Accumulation in ArABIdopsis
原文摘要:
Light is a major environmental cue affecting various physiological and metabolic processes in plants. Although plant photoreceptors are well characterized, the mechanisms by which light regulates downstream responses are less clear. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the accumulation of photo-protective anthocyanin pigments is light dependent and the R2R3 MYB transcription factor MYB75/PAP1 regulates anthocyanin accumulation. Here we report that MYB75 interacts with and is phosphorylated by MAP KINASE 4 (MPK4). Their interaction is dependent on MPK4 kinase activity and is required for full function of MYB75. MPK4 can be activated in response to light, and is involved in the light-induced accumulation of anthocyanins. We show that MPK4 phosphorylation of MYB75 increases its stability and is essential for light-induced anthocyanin accumulation. Our findings reveal an important role for a MAPK pathway in light signal transduction.
作者:邱金龙

