American Journal of Physiology:中科院昆明植物所熊文勇研究组发表脂肪
近日,国际期刊《American Journal of Physiology》杂志在线发表了中国科学院昆明植物研究所熊文勇研究组与李艳研究组合作的一篇研究论文,研究揭示了脂肪组织在体内能量平衡调节中发挥重要作用。体内脂肪累积过多不仅会导致肥胖进而引发2型糖尿病,还与高血压、高血脂、脂肪肝、心血管疾病以及部分癌症等疾病密切相关;然而脂肪过少又会引起脂肪萎缩症和其他代谢性疾病。
RACK1 (Receptor of activated protein kinase C) 是一个在真核生物中广泛表达且非常保守的胞内蛋白,在细胞分裂、凋亡、连接、迁移、应激反应、神经活动和生理节律等一系列生命过程中发挥重要作用,另外RACK1与胃癌、肝癌、肺癌等多种肿瘤的发生密切相关。但一直以来RACK1在脂肪细胞分化中的作用仍然未知。
近日,,利用经典的3T3-L1脂肪细胞分化模型首次对RACK1在脂肪分化过程中的作用进行了探索,发现RACK1的蛋白水平随着脂肪分化的进行逐步升高,knockdown RACK1会明显抑制脂肪细胞的分化,同时脂肪分化关键转录因子C/EBP-β和 PPAR-γ也明显下调;进一步研究发现RACK1 knockdown后激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路并抑制了PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K信号通路,表明RACK1通过调控Wnt/β-catenin和PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K信号通路来调节脂肪分化。基于脂肪组织在机体能量平衡调节中的重要作用,这些结果不仅为进一步阐明脂肪分化的分子机制提供了重要信息,也为相关代谢性疾病的预防和治疗提供了新的理论依据和分子靶点。
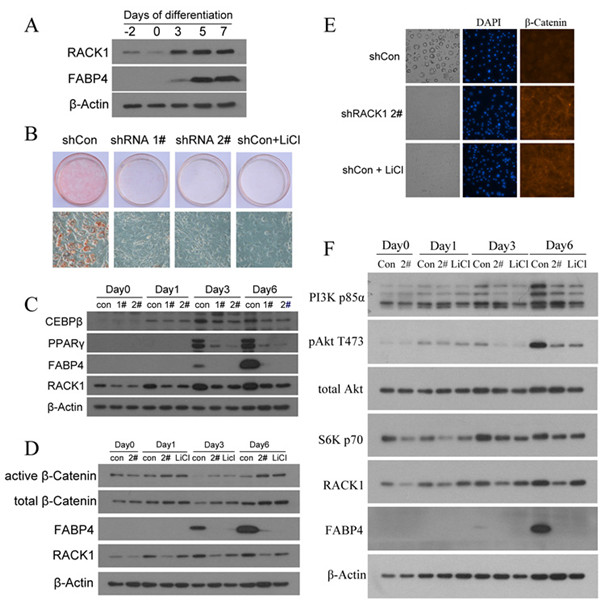
图:RACK1通过Wnt/β-catenin和PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K信号通路调节脂肪分化
原文链接:
RACK1 is required for adipoGENEsis
原文摘要:
Adipose tissue plays a critical role in metabolic diseases and the maintenance of energy homeostasis. RACK1 has been identified as an adaptor protein involved in multiple intracellular signal transduction pathways and diseases. However, whether it regulates adipogenesis remains unknown. Here, we reported that RACK1 is expressed in 3T3-L1 cells and murine white adipose tissue, and RACK1 knockdown by shRNA profoundly suppressed adipogenesis by reducing the expression of PPARγ and C/EBPβ. Depletion of RACK1 increased β-Catenin protein levels and activated Wnt signaling. Furthermore, RACK1 knockdown also suppressed the PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K signaling pathway by reducing the PI3K p85α, pAkt T473 and S6K p70. Taken together, these results demonstrated that RACK1 is a novel factor required for adipocyte differentiation by emerging Wnt/β-Catenin signaling and PI3K-Akt-mTOR-S6K signaling pathway(s).
DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00224.2016
作者:熊文勇

