Cancer Lett:中科院微生物所孟颂东课题组发布竞争性病毒RNA研究进
近日,国际癌症领域知名期刊《Cancer Letters》杂志在线发表了中国科学院微生物所题为“Hepatitis B virus mRNAs functionally sequester let-7a and enhance hepatocellular carcinoma”的研究论文,博士生邓蒙蒙是第一作者,孟颂东和李长菲是通讯作者。
众所周知,病毒RNA(或mRNA)的主要功能是作为模板翻译病毒蛋白,然而孟颂东课题组近几年发现病毒RNA的新功能,即作为竞争性病毒RNA(competitive virus RNA, cvRNA)直接参与调节病毒复制、感染和病理,cvRNA是该课题组提出的病毒与宿主相互作用的新模式。
课题组最近研究发现乙肝病毒的3个RNA(包括pgRNA, Pre-S和S mRNA)均含有宿主miRNA(微小RNA)let-7a的结合位点,可吸附和降解肝细胞中let-7a,进而引起let-7a的靶基因c-myc, K-RAS和CCR7等肿瘤基因表达的上调,从而促进肝癌的发生和进展。这为进一步揭示慢性乙肝感染引发肝癌发生的机制和发现治疗肝癌的新靶点提供了线索。这是该课题组在竞争性病毒RNA方面发表的第三篇论文,他们前期研究已经发现乙肝病毒RNA作为竞争性病毒RNA参与促进病毒复制、增强病毒适应肝细胞环境和诱导肝细胞癌发生。
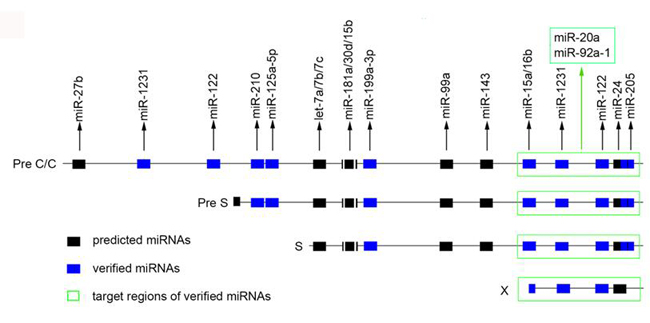
乙肝病毒pgRNA(Pre C/C)和Pre S、S、X mRNA与肝细胞中miRNA的结合位点
原文链接:
Hepatitis B virus mRNAs functionally sequester let-7a and enhance hepatoCellular carcinoma
原文摘要:
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection induces hepatocarcinogenesis and malignant progression, yet global effects of the redundant viral mRNAs produced during infection are unexplored. Here, microRNA (miRNA) target prediction and whole genome expression analysis revealed that HBV pre-C/C mRNA leads to upregulation of multiple let-7a targeted genes. A let-7a complementary region from nt 86 to 108 in the HBV genome was then identified in HBV pre-C/C, pre-S, and S mRNAs. The let-7a sequestration effect by HBV mRNAs was observed under transfection and virus infection, which is dependent on the let-7a response sequence. Moreover, we found reduced AGO2 binding, as well as functional mRNA and protein de-repression of let-7a targets (e.g., c-myc, K-RAS, and CCR7), upon viral mRNA expression. Let-7a levels in the liver were significantly decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with HBV infection and were negatively correlated with intrahepatic pre-S2 mRNA levels. Finally, both in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that let-7a inhibition by HBV mRNAs resulted in enhanced HCC cell colony formation and tumor growth, providing evidence of the oncogenic potential of HBV mRNAs.
doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.028
作者:孟颂东

