PLOS Biology:中科院遗传所王永红和李家洋研究组发表拟南芥MAPK信
2016年9月12日,国际著名学术杂志《PLOS biology》上在线发表了中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所王永红研究组和李家洋组研究组合作的在拟南芥MAPK信号途径最新研究发现,李家洋和王永红研究组已毕业的博士研究生贾伟彦、李宝华和助理研究员黎舒佳博士为该论文的共同第一作者,王永红研究员和李家洋研究员为共同通讯作者。
促分裂原活化激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)级联信号途径是真核生物中普遍存在的重要信号转导通路,它通过复杂的信号转导过程将外源刺激准确地转变为细胞内的生理反应,从而调控生物体诸多重要的生物学过程。MAPK级联信号途径的特异性调控是当前MAPK级联信号研究最为关注的问题之一。
研究报道了拟南芥MKK7在体内和体外可以特异性地磷酸化MPK3和MPK6。遗传学结果表明,MKK7-MPK6信号通路特异性地参与调控叶脉的形态建成、重力反应、花丝伸长、侧根形成及分枝发育,而MKK7-MPK3途径则在调控叶片形态中发挥重要作用。进一步研究发现,MKK7-MPK6级联信号通过磷酸化PIN-FORMED 1(PIN1)的Ser337位点,调控了PIN1在体内的极性定位,从而调控了由生长素极性运输介导的植株的分枝发育。上述研究结果揭示了MKK7-MPK6级联信号途径特异性调控植株分枝发育的重要机制。首次将MAPK级联信号与PIN蛋白磷酸化介导的极性定位联系起来,无论在MAPK级联信号的特异性研究还是在PIN蛋白极性定位的调控机理研究领域都是创新性的发现,并为深入解析生长素极性运输调控植物生长发育的分子机制开拓了新的视野。
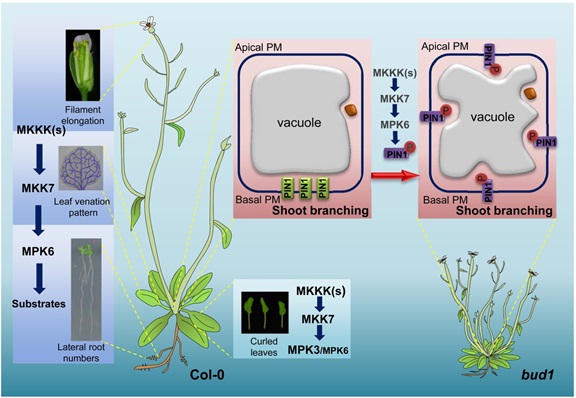
拟南芥MKK7-MPK6/3级联信号调控植株生长发育的模式图
原文链接:
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Cascade MKK7-MPK6 Plays Important Roles in plant Development and Regulates Shoot Branching by Phosphorylating PIN1 in Arabidopsis
原文摘要:
Emerging evidences exhibit that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/MPK) signaling pathways are connected with many aspects of plant development. The complexity of MAPK cascades raises challenges not only to identify the MAPK module in planta but also to define the specific role of an individual module. So far, our knowledge of MAPK signaling has been largely restricted to a small subset of MAPK cascades. Our previous study has characterized an Arabidopsis bushy and dwarf1 (bud1) mutant, in which the MAP Kinase Kinase 7 (MKK7) was constitutively activated, resulting in multiple phenotypic alterations. In this study, we found that MPK3 and MPK6 are the substrates for phosphorylation by MKK7 in planta. Genetic analysis showed that MKK7-MPK6 cascade is specifically responsible for the regulation of shoot branching, hypocotyl gravitropism, filament elongation, and lateral root formation, while MKK7-MPK3 cascade is mainly involved in leaf morphology. We further demonstrated that the MKK7-MPK6 cascade controls shoot branching by phosphorylating Ser 337 on PIN1, which affects the basal localization of PIN1 in xylem parenchyma cells and polar auxin transport in the primary stem. Our results not only specify the functions of the MKK7-MPK6 cascade but also reveal a novel mechanism for PIN1 phosphorylation, establishing a molecular link between the MAPK cascade and auxin-regulated plant development.
doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002550
作者:王永红和李家洋

