Plant Physiol:中科院版纳植物园余迪求研究组揭示植物激素赤霉素
2016年7月12日,国际植物学顶级期刊《plant Physiology》杂志上在线发表了中国科学院西双版纳热带植物园分子生物学研究组和植物环境适应性研究组合作题为以The DELLA-CONSTANS transcription factor cascade integrates gibberelic acid and photoperiod signaling to regulate flowering的研究论文,博士研究生王后平为该论文的第一作者,胡彦如副研究员和余迪求研究员为该论文的通讯作者。相关阅读:Plant Physiol:中科院版纳植物园余迪求研究组揭示WRKY57参与调控植物激素茉莉酸信号转导及抗病性的分子机理
植物激素赤霉素与光周期途径协同调控开花诱导的信号转导机理植物激素是植物体内重要的生长调节物质,广泛参与调控植物的生长发育和抗逆境反应。在模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中,赤霉素激素(Gibberellin,GA)促进植物的开花诱导过程。目前研究表明,GA可与光周期(Photoperiod)信号协同调控植物在长日照条件下的开花诱导;然而,GA和光周期信号在植物开花诱导过程中的相互作用机理仍不清楚。
研究发现,GA诱导成花素基因FT的表达依赖于光周期信号途径中的关键转录因子CO蛋白。分子生物学及生物化学实验表明,GA途径的抑制子DELLA蛋白能与CO相互作用形成蛋白复合物,并抑制其转录激活功能。进一步遗传学研究表明,DELLA蛋白抑制植物开花诱导部分依赖于CO/FT介导的光周期信号途径。该研究证实GA途径的抑制子DELLA蛋白能直接抑制光周期途径中的关键转录因子CO,从而协同调控植物在长日照条件下的开花诱导过程。
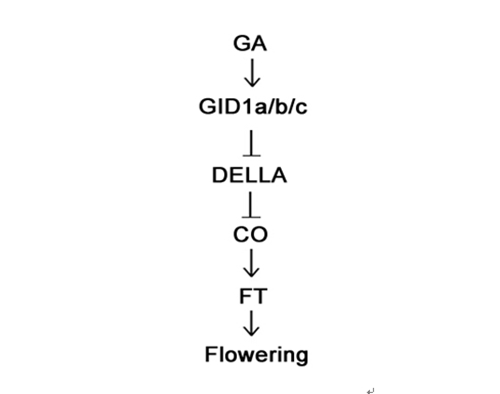
植物激素赤霉素与光周期途径协同调控植物开花诱导的工作模型
原文链接:
The DELLA-CONSTANS transcription factor cASCade integrates gibberelic acid and photoperiod signaling to regulate flowering
原文摘要:
Gibberellin (GA) and photoperiod pathways have recently been demonstrated to collaboratively modulate flowering under long-days (LDs). However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this collaboration remain largely unclear. In this study, we found that GA-induced expression of FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) under LDs was dependent on CONSTANS (CO), a critical transcription factor positively involved in photoperiod signaling. Mechanistic investigation revealed that DELLA proteins, a group of crucial repressors in GA signaling, physically interacted with CO. The DELLA-CO interactions repressed the transcriptional function of CO protein. Genetic analysis demonstrated that CO acts downstream of DELLA proteins to regulate flowering. Disruption of CO rescued the earlier-flowering phenotype of the gai-t6 rga-t2 rgl1-1 rgl2-1 mutant (dellap), while a gain-of-function mutation in GA INSENSITIVE (GAI, a member of the DELLA gene) repressed the earlier-flowering phenotype of CO-overexpressing plants. In addition, the accumulation of DELLA proteins and mRNAs was rhythmic, and REPRESSOR OF GA1-3 (RGA) protein was noticeably decreased in the long-day afternoon, a time when CO protein is abundant. Collectively, these results demonstrate that the DELLA-CO cascade inhibits CO/FT-mediated flowering under LDs, which thus provide evidence to directly integrate GA and photoperiod signaling to synergistically modulate flowering under LDs.
作者:余迪求

